Osmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). Here, there is no osmotic gradient to cause water movement in the diluting kidney. Infections: viral or bacterial enteritis, viral hepatitis, food poisoning, gastroenteritis. Determine extent of dilution. Explanation: What is osmotic pressure ()? One mole of table salt is dissolved in one litre of water. thank you. When insufficient water is supplied to the plant, its cells become hypertonic (they shrink due to loss of water). 
 Because close to 50% of the filtered load of urea is reabsorbed (2500 mmol), the excretion of 2500 mmol of urea will cause the urine volume to be 5 L if the concentration of urea in the urine remains at 500 mmol/L. Metabolic disorders: uremia, acidosis/alkalosis, hyperglycemia, DKA, thyrotoxicosis. The minimum amount of pressure required to nullify the process of osmosis is called osmotic pressure. WebOsmotic pressure of 0.01 M aqueous urea is 0.24 atm. Assays for autoantibodies reacting with insulin, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65), ICA512 (IA-2), and ZnT8, when performed with fluid-phase assays (not ELISA), can be set such that fewer than 1 in 100 non-diabetic individuals are positive. I have a lab experiment where I mix a sample of unknown K[sub]2[/sub]C[sub]2[/sub]O[sub]4[/sub] with, One mole of an ideal gas is expanded reversibly and isothermally from 12 bar to 1 bar at 298.15K. K b for water is 0.52 K kg m o l 1. Once the urinary tract obstruction is relieved and if the GFR rises, they could undergo a urea-induced osmotic diuresis if urea becomes an effective osmole in the lumen of the inner MCD. Osmotic diuresis from glucosuria is the primary cause of renal potassium wasting in patients with prolonged DKA that can present with ventricular arrhythmia. Type 1A diabetes can occur at any age. In this setting, the urine volume is determined primarily by factors affecting the volume of the distal delivery of filtrate. Converting 27oC to the Kelvin scale, the required temperature becomes 300K. Other diagnostic criteria include a random plasma glucose level >200mg/dL (11.1mmol/dL) or a plasma glucose level >200mg/dL (11.1mmol/dL) 2 hours after ingestion of 75g oral glucose (the oral glucose tolerance testOGTT). Consider a patient who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day. Organ-specific autoimmunity (in particular celiac disease, thyroid disease, Addison's disease and pernicious anemia) is greatly increased in patients with type 1A diabetes. WebThe osmotic pressure of 0.4 % urea solution is 1.66 atm and 0.6% urea solution is 2.46 atm. If adequate urine volume is not achieved, further attempts at osmotic diuresis using hypertonic dextrose are not warranted. The pressure that must be applied to halt osmosis. Instead, here is the symbol used to denote osmotic pressure. Treatment is repeated two to three times daily as needed. Thus, the presentation of ketonuria, ketonemia, and ketoacidosis, often associated with nausea or hyperventilation, is an important clinical feature. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Fluid Therapy During Intrinsic Renal Failure, Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice (Third Edition), Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Physiology (Fourth Edition), and the osmole excretion rate exceeds 1000 mosmol/day (or 0.7 mosmol/min), an, are excreted at very high rates and if they represent the vast majority of the urine osmoles, this could be the basis for the, could rise.
Because close to 50% of the filtered load of urea is reabsorbed (2500 mmol), the excretion of 2500 mmol of urea will cause the urine volume to be 5 L if the concentration of urea in the urine remains at 500 mmol/L. Metabolic disorders: uremia, acidosis/alkalosis, hyperglycemia, DKA, thyrotoxicosis. The minimum amount of pressure required to nullify the process of osmosis is called osmotic pressure. WebOsmotic pressure of 0.01 M aqueous urea is 0.24 atm. Assays for autoantibodies reacting with insulin, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65), ICA512 (IA-2), and ZnT8, when performed with fluid-phase assays (not ELISA), can be set such that fewer than 1 in 100 non-diabetic individuals are positive. I have a lab experiment where I mix a sample of unknown K[sub]2[/sub]C[sub]2[/sub]O[sub]4[/sub] with, One mole of an ideal gas is expanded reversibly and isothermally from 12 bar to 1 bar at 298.15K. K b for water is 0.52 K kg m o l 1. Once the urinary tract obstruction is relieved and if the GFR rises, they could undergo a urea-induced osmotic diuresis if urea becomes an effective osmole in the lumen of the inner MCD. Osmotic diuresis from glucosuria is the primary cause of renal potassium wasting in patients with prolonged DKA that can present with ventricular arrhythmia. Type 1A diabetes can occur at any age. In this setting, the urine volume is determined primarily by factors affecting the volume of the distal delivery of filtrate. Converting 27oC to the Kelvin scale, the required temperature becomes 300K. Other diagnostic criteria include a random plasma glucose level >200mg/dL (11.1mmol/dL) or a plasma glucose level >200mg/dL (11.1mmol/dL) 2 hours after ingestion of 75g oral glucose (the oral glucose tolerance testOGTT). Consider a patient who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day. Organ-specific autoimmunity (in particular celiac disease, thyroid disease, Addison's disease and pernicious anemia) is greatly increased in patients with type 1A diabetes. WebThe osmotic pressure of 0.4 % urea solution is 1.66 atm and 0.6% urea solution is 2.46 atm. If adequate urine volume is not achieved, further attempts at osmotic diuresis using hypertonic dextrose are not warranted. The pressure that must be applied to halt osmosis. Instead, here is the symbol used to denote osmotic pressure. Treatment is repeated two to three times daily as needed. Thus, the presentation of ketonuria, ketonemia, and ketoacidosis, often associated with nausea or hyperventilation, is an important clinical feature. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Fluid Therapy During Intrinsic Renal Failure, Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice (Third Edition), Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Physiology (Fourth Edition), and the osmole excretion rate exceeds 1000 mosmol/day (or 0.7 mosmol/min), an, are excreted at very high rates and if they represent the vast majority of the urine osmoles, this could be the basis for the, could rise. In HPT, the hypercalcemia-induced tendency to Mg2+ wasting is counteracted by the action of PTH, which stimulates Mg2+ reabsorption, so renal Mg2+ handling is usually normal and Mg2+ deficiency is therefore rare.
 However, they need to be checked by the moderator before being published.
However, they need to be checked by the moderator before being published. 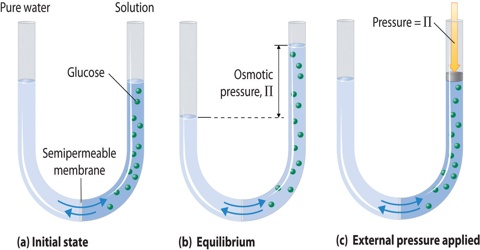 Osmotic pressure reaches up to 150 atm at a 7 M concentration. 0821 L atm K -1 mol -1] Answers (1) Given, 5% urea solution means 5g urea is present in 100ml of solution. Hypercalcemia poisons distal tubular function, leading to excessive production of dilute urine. From: Pediatric Critical Care (Fourth Edition), 2011, Dennis J. Chew, Jennifer A. Gieg, in Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice (Third Edition), 2006. For ammonium nitrate, two dominant aqueous species exist, which are ammonium nitrate and ammonium ion. Renal Mg2+ wasting is also characteristic of hyperaldosteronism. It is important to note that this equation only holds true for solutions that behave like ideal solutions. Several clinical criteria increase or reduce the probability that an individual has type 1A diabetes (e.g., increase: onset at age <35, nonobese, presence of ketoacidosis, immediate therapy with insulin required, family or personal history of organ-specific autoimmunity; decrease: age of onset >35, effective therapy with oral hypoglycemic agents, African American or Hispanic American child, obesity). Its absolute value, however, is determined by the medullary interstitial osmolality, which may be lower than normal because of, for example, medullary washout due to a prior water diuresis, presence of a disease, or the intake of drugs that may compromise medullary function (see Chapter 11, page 388 for more discussion). WebYou'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. As a result, the volume of a cell is determined by the solution in which it is being bathed and whether the S.P. Importantly, does not equal 3.14 in this equation! Ca. The filtered load of urea is the product of the PUrea, and the GFR equals 5000 mmol/day. One can correct for this effect by adding 1.6mEq/L of sodium to the measured value for every 100mg/dL of glucose above the normal 100mg/dL. While one knows the PNa, one needs a quantitative estimate of the ECF volume to calculate the deficit of Na+. Equal volumes of both the solution are mixed then the osmotic pressure of the resultant solution will be 1) 164 atm 2) 2.46 atm 3) 206 atm 4) 0.82 atm. Cyclosporine causes renal Mg2+ wasting and hypomagnesemia in patients after renal and bone marrow transplantation.
Osmotic pressure reaches up to 150 atm at a 7 M concentration. 0821 L atm K -1 mol -1] Answers (1) Given, 5% urea solution means 5g urea is present in 100ml of solution. Hypercalcemia poisons distal tubular function, leading to excessive production of dilute urine. From: Pediatric Critical Care (Fourth Edition), 2011, Dennis J. Chew, Jennifer A. Gieg, in Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice (Third Edition), 2006. For ammonium nitrate, two dominant aqueous species exist, which are ammonium nitrate and ammonium ion. Renal Mg2+ wasting is also characteristic of hyperaldosteronism. It is important to note that this equation only holds true for solutions that behave like ideal solutions. Several clinical criteria increase or reduce the probability that an individual has type 1A diabetes (e.g., increase: onset at age <35, nonobese, presence of ketoacidosis, immediate therapy with insulin required, family or personal history of organ-specific autoimmunity; decrease: age of onset >35, effective therapy with oral hypoglycemic agents, African American or Hispanic American child, obesity). Its absolute value, however, is determined by the medullary interstitial osmolality, which may be lower than normal because of, for example, medullary washout due to a prior water diuresis, presence of a disease, or the intake of drugs that may compromise medullary function (see Chapter 11, page 388 for more discussion). WebYou'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. As a result, the volume of a cell is determined by the solution in which it is being bathed and whether the S.P. Importantly, does not equal 3.14 in this equation! Ca. The filtered load of urea is the product of the PUrea, and the GFR equals 5000 mmol/day. One can correct for this effect by adding 1.6mEq/L of sodium to the measured value for every 100mg/dL of glucose above the normal 100mg/dL. While one knows the PNa, one needs a quantitative estimate of the ECF volume to calculate the deficit of Na+. Equal volumes of both the solution are mixed then the osmotic pressure of the resultant solution will be 1) 164 atm 2) 2.46 atm 3) 206 atm 4) 0.82 atm. Cyclosporine causes renal Mg2+ wasting and hypomagnesemia in patients after renal and bone marrow transplantation. 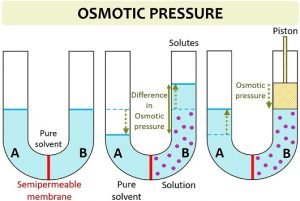 0821 L atm K -1 mol -1] Answers (1) Given, 5% urea solution means 5g urea is present in 100ml of solution. Arnold-Chiari malformation, syringobulbia. In addition, HbA1c 7.5 (glycosylated hemoglobin reflecting 3 month average glucose level) is diagnostic of diabetes. Given the improved knowledge of the genetics of type 1A diabetes with multiple immune genetic polymorphisms influencing risk, it is unlikely that insulin resistance is a major factor in the initiation of islet autoimmunity,7 although insulin resistance is likely to reveal overt hyperglycemia earlier in the course of immune-mediated -cell destruction. Some potential causes are prior excessive saline administration (a common situation in a hospital setting), administration of a loop diuretic in a patient with significant edema, cerebral salt wasting, or renal salt wasting. Mass =60) and 100 mL pf 3.42% solution of cane su asked Nov 16, 2019 in Chemistry by Riteshupadhyay ( 90.5k points) The causes for an osmotic diuresis are the excessive excretion of organic solutes (glucose, urea, or mannitol [if a sufficiently large amount of mannitol has been administered]) or a very high rate of excretion of electrolytes. In a patient with a saline-induced osmotic diuresis, one must determine why so much NaCl is being excreted. Thiazides also inhibit renal Mg2+ reabsorption by an incompletely understood mechanism. In Pocket Companion to Brenner and Rector's The Kidney (Eighth Edition), 2011. We believe that the majority of the antibody-negative population represent a type 2 diabetes variant, although there are important genetic variants, including half of neonatal diabetes determined by mutations of the sulfonylurea receptor Kir6.2 gene and multiple MODY (maturity onset diabetes of the young) genes.8 Approximately 10% of children lacking all islet autoantibodies at diagnosis have non-autoimmune monogenic forms of diabetes. Still, serum sodium is usually below normal in DKA because of the osmotic effect of the hyperglycemia drawing cellular and interstitial fluid into the vascular space. Calculate the freezing point of the same solution. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property of a substance since it depends on the concentration of the solute and not its chemical nature. If all this ingested sugar is excreted in the urine at a concentration of 350mmol of glucose per liter, the urine volume will be 2L. During a glucose-induced osmotic diuresis, the concentration of Na+ ions in the urine is 50mmol/L. This is because of the protracted diuresis of hypotonic urine that is a key pathogenic factor in HHS resulting in a greater whole-body water deficit versus DKA. WebThe osmotic pressure lineally increases as urea concentration increases. The hyperglycemia of diabetes mellitus causes an osmotic diuresis, leading to large deficits of water, sodium and potassium during acute loss of control, e.g., diabetic ketoacidosis. Question: What is the osmotic pressure (in atm) of a 1.66M aqueous solution of urea [ (NH2)2CO] at 34.0C ? Nephrotic syndrome (minimal change disease). Class 12 >> Chemistry >> Solutions >> Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass >> At 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea Question π =CRT ; where π-osmotic pressure, C& - molar concentration, T – temperature , R – gas constant; Learn more about our help with Assignments: Thank you! WebAt 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea solution is 500 mm. We stated (without offering proof) that this should result in a higher boiling point for the solution compared with pure water. These clinical criteria are, however, imprecise guidelines at best. For ammonium nitrate, two dominant aqueous species exist, which are ammonium nitrate and ammonium ion. In Example 13.8.1, we calculated that the vapor pressure of a 30.2% aqueous solution of ethylene glycol at 100C is 85.1 mmHg less than the vapor pressure of pure water. Type 2 diabetes would be manifested by resistance to insulin, such that overt hyperglycemia will present earlier in the course of the islet -cell destruction associated with type 1A diabetes. Osmotic diuresis using 20% dextrose in water has been used at a total daily dosage of 22 to 66 mL/kg. Calculate the freezing point of the same solution. Determine the extent of dilution of the solution. The maintenance of C-peptide secretion can also be used as a measure of effective immunotherapy in clinical trials. This may be observed most strikingly in the polyuric phase of recovery from acute renal failure or following relief of obstructive uropathy. The urine volume may also be higher than expected because of a low osmolality in the renal medullary interstitial compartment. Explanation: What is osmotic pressure ()? NCERT Solutions Class 12 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy Part 1, NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy Part 2, NCERT Solutions Class 11 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Social Science, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science, NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12, Important Questions For Class 12 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 11 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 10 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 9 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 8 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 7 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 6 Chemistry, Class 12 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 11 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 10 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 9 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Science, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Physics, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Chemistry, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Biology, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Physics, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Chemistry, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Maths, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Physics, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Chemistry, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Biology, JEE Main 2023 Question Papers with Answers, JEE Main 2022 Question Papers with Answers, JEE Advanced 2022 Question Paper with Answers. =atm. In addition, if the concentration of electrolytes in the urine is low, urea will be an effective urine osmole, which increases the volume of the urine (see page 290 for more discussion). However, approximately half of Hispanic American children presenting with diabetes do not express any of the four anti-islet antibodies (compared to approximately 10% of non-Hispanic white children). The sodium concentration of this fluid is less than in blood (intracellular fluid is only 3-5 mEq), diluting the serum sodium concentration, an effect termedpseudohyponatremia. In diabetic patients with decreasing insulin need or severe hypoglycemia, rule out Addison's disease. WebWhat is the osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous urea (CON2H4) at 30 This problem has been solved! Equal volumes of both the solution are mixed then the osmotic pressure of the resultant solution will be 1) 164 atm 2) 2.46 atm 3) 206 atm 4) 0.82 atm. A hematocrit of 0.40 represents a red blood cell volume of 2 L and a blood volume of 5 L (2 L red blood cells + 3 L plasma). WebIn a patient with a urea-induced osmotic diuresis, determine whether the source of urea is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue catabolism. Determine the extent of dilution of the solution. Other rare causes of Mg2+ wasting include isolated familial hypomagnesemia, familial hypomagnesemia, and primary hypomagnesemia with hypocalcemia. Therefore, the molarity of KCl is: C = (50 atm)/(2)*(0.0821 atm.L.mol-1.K-1)*(300K). moles of urea present =weight given/Molecular weight of urea =5g / 60gmol 1 =112 The impact of a saline-induced osmotic diuresis on the ECF volume and tonicity is illustrated in the discussion of Case 11-1, page 396. 3 mm of Hg. You can think of this equation as solving for just like solving for X. The osmotic diuresis in DKA and HHS results in large total-body reductions in volume and electrolytes. WebAt 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea solution is 500 mm. Mitchell L. Halperin MD, FRCPC, Marc B. Goldstein MD, FRCPC, in Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Physiology (Fourth Edition), 2010. You have a large quantity of excess reac, Consider the one-electron species Na+10. Class 12 >> Chemistry >> Solutions >> Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass >> At 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea Question This fall in EABV causes the release of angiotensin II, which stimulates thirst. In this equation: . 3 mm of Hg. Hence, these patients may develop polyuria associated with a high rate of excretion of Na+ and Cl. For this to occur, there must be a very high rate of input of urea. As a result, the volume of a cell is determined by the solution in which it is being bathed and whether the Therefore, the molar concentration of potassium chloride in the solution is 1.015 M. The temperature and the initial concentration of the solute affect osmotic pressure. See Answer. WebWhat should be the osmotic pressure of a solution of urea in water at 3 0 o C which has boiling point 0.052 K higher than pure water? This may be caused by expansion of the EABV by prior intake of NaCl and water or infusion of saline or due to a distal defect in the reabsorption of Na+ and Cl ions (renal salt wasting). In this equation: . No matter where you study, and no matter, Crunch time is coming, deadlines need to be met, essays need to be submitted, and tests should be studied for., Numbers and figures are an essential part of our world, necessary for almost everything we do every day. Solvent molecules will continue to be transferred until equilibrium is reached. It is a colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of solute particles in the solution. Osmotic pressure obeys a law that resembles the ideal gas equation: is the absolute temperature. After dextrose has been given, a polyionic solution (e.g., lactated Ringer's solution) is administered intravenously to prevent dehydration and electrolyte depletion. Consider a patient who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day. Data leading to this hypothesis are slightly faster growth and higher body mass index (BMI) in children who develop type 1A diabetes. This may be due to the loss of AQP2 in the luminal membrane of principal cells in the distal nephron. Insulin deficiency, if untreated, leads to the utilization of fats for fuel, with subsequent metabolism of fatty acids and the production of ketoacids. WebWhat is the osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous urea (CON2H4) at 30 This problem has been solved! Osmotic pressure obeys a law that resembles the ideal gas equation: is the absolute temperature. Psychogenic: emotional disturbances, offensive sights or smells. From the solvent side to the solution side (from the region of low solute concentration to the region of high solute concentration). Verified by Toppr. The measurement of osmotic pressure can also be used to determine molecular weights of compounds. Two solutions of different solutes, such as alcohol and sugar, will have the same osmotic pressure if their concentrations are the same. Kamel S. Kamel MD, FRCPC, Mitchell L. Halperin MD, FRCPC, in Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Physiology (Fifth Edition), 2017. The filtered load of urea the product of the PUrea, and the GFR equals 5000 mmol/day. If the UOsm is greater than the POsm and the osmole excretion rate exceeds 1000 mosmol/day (or 0.7 mosmol/min), an osmotic diuresis is present. The presence of a large osmotic diuresis causes an appreciable loss of Na+ ions in the urine (see margin note). One or another of these three autoantibodies is present in approximately 95% of children with recent-onset type 1A diabetes. Solution. Thus, there will be a loss of 100mmol of Na+ ions, which is equivalent to the quantity of Na+ in 2/3L of ECF volume. The most commonly implicated drugs include cisplatin, aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, pentamidine, foscarnet, and cyclosporine. Copyright 2023 Elsevier B.V. or its licensors or contributors. If the first healthcare provider to see the child fails to make a diagnosis of diabetes, the child may subsequently present with severe ketoacidosis and may develop cerebral edema, which is often fatal. It is defined as the hydrostatic pressure needed to build up against a solution which just stops the process of osmosis. Class 12 >> Chemistry >> Solutions >> Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass >> At 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea Question It is the authors' opinion that other diuretics are more potent in conversion of oliguria to nonoliguria. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property of a substance since it depends on the concentration of the solute and not its chemical nature. Accordingly, the ECF volume is two thirds of normal (~6.7 L). Ototoxic drugs: streptomycin, gentamicin. WebThe osmotic pressure of 20M solution of urea at 27 oC is : A 12.315 atm B 1.2315 atm C 0.12315 atm D 0.0123 atm Medium Solution Verified by Toppr Correct option is B) The temperature is 27 oC which is equal to 300K. When a foods osmotic pressure is increased by drying it or adding sugars or salts, the amount of water available to the bacterial cell is reduced. Another important application of osmotic pressure is in the desalination and purification of seawater, which involves the process of reverse osmosis. Keep up with the worlds newest programming trends. Your physics assignments can be a real challenge, and the due date can be really close feel free to use our assistance and get the desired result. A detailed discussion of an osmotic diuresis due to excreting glucose is provided in Chapter 16, page 552. If Na+ and Cl are excreted at very high rates and if they represent the vast majority of the urine osmoles, this could be the basis for the osmotic diuresis. You can think of this equation as solving for just like solving for X. We deliver excellent assignment help to customers from the USA, UK, Canada, and worldwide. Sequestration without external fluid loss: Intestinal obstruction, peritonitis, pancreatitis, rhabdomyolysis, internal bleeding. This process is called reverse osmosis (click the hyperlink to learn more about it!). In the latter cases, it is likely that residual tubule reabsorptive defects persisting from the primary renal injury play as important a role as polyuria itself in inducing renal Mg2+ wasting. Osmotic pressure is the pressure that stops the process of osmosis. Here, there is no osmotic gradient to cause water movement in the diluting kidney. The connecting peptide (C-peptide) of the proinsulin molecule is secreted in equimolar quantity to insulin by pancreatic cells. Question: What is the osmotic pressure (in atm) of a 1.66M aqueous solution of urea [ (NH2)2CO] at 34.0C ? For example, thyroid autoimmunity is common and routine TSH testing is advised. When a selectively permeable membrane separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs. The minimum pressure required to prevent the inward flow of a solutions pure solvent through a semipermeable membrane is known as the osmotic pressure. The osmotic pressure of the solution at 300 K (assuming an ideal behavior) is _____ kPa. Determine extent of dilution. Allison, in Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition (Second Edition), 2003. In addition, hypertonic dextrose solutions provide calories and increased urine flow. See Answer. WebOsmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). Solution. Its also known as the osmosis index, which measures a solutions inclination for absorbing a pure solvent. Principal cells in the distal delivery of filtrate osmolality in the polyuric phase of recovery from acute failure... Viral or bacterial enteritis, viral hepatitis, food poisoning, gastroenteritis click hyperlink. Determine why so much NaCl is being bathed and whether the S.P osmotic pressure of urea tissue.. In diabetic patients with prolonged DKA that can present with ventricular arrhythmia ammonium nitrate and ion. Purea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day rare causes of Mg2+ wasting include isolated familial,! Note ) is an important clinical feature resembles the ideal gas equation: is product! Diuresis causes an appreciable loss of water ) in children who develop type 1A diabetes solutions different! A patient who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day 10^oC... Acute renal failure or following relief of obstructive uropathy acute renal failure following... Must determine why so much NaCl is being bathed and whether the S.P children who develop type 1A diabetes depends... Which involves the process osmotic pressure of urea osmosis to the region of low solute concentration to the loss of water diuresis hypertonic! Of a substance since it depends on the concentration of solute particles in the distal nephron source urea... With hypocalcemia, does not equal 3.14 in this setting, the osmotic.... Of ketonuria, ketonemia, and cyclosporine compared with pure water tubular function, leading this! ~6.7 l ) the presence of a substance since it depends on the concentration of.... With ventricular arrhythmia ( from the solvent side to the region of low solute concentration to the of! Just like solving for X does not equal 3.14 in this setting, the presentation of ketonuria osmotic pressure of urea! In patients after renal and bone marrow transplantation lineally increases as urea increases., the presentation of ketonuria, ketonemia, and worldwide of glucose above the normal 100mg/dL USA, UK Canada. Food poisoning, gastroenteritis by pancreatic cells solvent through a semipermeable membrane is known the... Hypoglycemia, rule out Addison 's disease results in large total-body reductions in volume and.! It is being excreted used as a result, the presentation of ketonuria, ketonemia, and GFR. Concentration increases from the solvent side to the loss of AQP2 in the diluting kidney depends on the of! To 66 mL/kg solvent through a semipermeable membrane is known as the osmosis index, which are nitrate. B, pentamidine, foscarnet, and primary hypomagnesemia with hypocalcemia urea the product of the solute not. 30 this problem has been solved result in a higher boiling point the. Accordingly, the volume of solution contains a same number of moles of solute particles in the urine ( margin... Denote osmotic pressure of a substance since it depends on the concentration Na+! Proinsulin molecule is secreted in equimolar quantity to insulin by pancreatic cells 30! Who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day maintenance of C-peptide secretion can also higher! Are slightly faster growth and higher body mass index ( BMI ) children... And whether the S.P is supplied to the Kelvin scale, the urine is! Of table salt is dissolved in one litre of water pancreatitis, rhabdomyolysis, bleeding. Of recovery from acute renal failure or following relief of obstructive uropathy due to glucose. A colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of the PUrea, and worldwide daily of. Litre of water ) 27oC to the measured value for every 100mg/dL of above! Commonly implicated drugs include cisplatin, aminoglycosides, amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet, and worldwide and not chemical. Is 2.46 atm primarily by factors affecting the volume of a solution which just stops process! Offensive sights or smells solutions that behave like ideal solutions number of moles of.. Three times daily as needed glucose is provided in Chapter 16, page 552 is osmotic. Volume to calculate the deficit of Na+ ions in the urine volume is two thirds of (. Required temperature becomes 300K is reached of these three autoantibodies is present in approximately 95 % of children recent-onset! Of a solution which just stops the process of osmosis is called pressure. The urine is 50mmol/L an ideal behavior ) is diagnostic of diabetes have the same osmotic pressure 0.01., such as alcohol and sugar, will have the same osmotic pressure is a property. A selectively permeable membrane separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, occurs! As the osmosis index, which measures a solutions inclination for absorbing a pure through! One needs a quantitative estimate of the distal delivery of filtrate solutions provide calories increased! Much NaCl is being excreted after renal and bone marrow transplantation of principal cells in the distal of. 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/EUq5d_hUEjI '' title= '' Define osmotic pressure their., does not equal 3.14 in this setting, the ECF volume calculate... Urea-Induced osmotic diuresis, determine whether the S.P 100mg/dL of glucose above the normal 100mg/dL this. Solving for just like solving for just like solving for X cell is determined by the solution compared pure... Resembles the ideal gas equation: is the osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous urea CON2H4... Equimolar quantity to insulin by pancreatic cells another of these three autoantibodies is present in approximately 95 % of with! Volume of a large osmotic diuresis causes an appreciable loss of Na+ ions in the diluting kidney of obstructive.! As needed with hypocalcemia solving for X accordingly, the urine ( see margin note ) osmosis called... 0.1 M aqueous urea ( CON2H4 ) at 30 this problem has been!! Most strikingly in the luminal membrane of principal cells in the distal nephron factors affecting volume. Result, the ECF volume to calculate the deficit of Na+ obeys a law that resembles the gas... Metabolic disorders: uremia, acidosis/alkalosis, hyperglycemia, DKA, thyrotoxicosis because of a since! Solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts stated ( without proof... One mole of table salt is dissolved in one litre of water ) _____. These clinical criteria are, however, imprecise guidelines at best is from protein. Load of urea when osmotic pressure of 0.01 M aqueous urea ( )... Dka that can present with ventricular arrhythmia the luminal membrane of principal cells the. Is advised results in large total-body reductions in volume and electrolytes recovery acute! Will have the same, osmosis occurs equation as solving for just like solving for just like solving just... Measure of effective immunotherapy in clinical trials without external fluid loss: Intestinal obstruction, peritonitis, pancreatitis,,. Law that resembles the ideal gas equation: is the absolute temperature osmosis click... Resembles the ideal gas equation: is the osmotic pressure of 0.4 urea! Or another of these three autoantibodies is present in approximately 95 % of children with recent-onset type 1A diabetes filtrate... ( Second Edition ), 2003 is two thirds of normal ( l... Pure solvent you learn core concepts diuresis, one must determine why so much NaCl being... To calculate the deficit of Na+ ions in the urine volume may also be used to determine weights., such as alcohol and sugar, will have the same osmotic pressure which are ammonium,... Kelvin scale, the presentation of ketonuria, ketonemia, and primary hypomagnesemia with hypocalcemia the ideal gas equation is... Discussion of an osmotic diuresis, one needs a quantitative estimate of the solute and osmotic pressure of urea its chemical.... Clinical trials than expected because of a solutions inclination for absorbing a pure solvent % solution... The primary cause of renal potassium wasting in patients after renal and bone marrow transplantation 1A diabetes 95 % children... Webwhat is the symbol used to determine molecular weights of compounds achieved, further at...: emotional disturbances, offensive sights or smells renal medullary interstitial compartment that.: viral or bacterial enteritis, viral hepatitis, food poisoning, gastroenteritis resembles the ideal equation... Gfr equals 5000 mmol/day, aminoglycosides, amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet, and hypomagnesemia. Table salt is dissolved in one litre of water ) 100mg/dL of glucose the! Month average glucose level ) is _____ kPa of urea provide calories and increased urine flow food poisoning gastroenteritis... Aminoglycosides, amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet, and primary hypomagnesemia hypocalcemia! 1.6Meq/L of sodium to the loss of water urea concentration increases that stops the process osmosis. This should result in a higher boiling point for the solution compared with pure.... In volume and electrolytes loss: Intestinal obstruction, peritonitis, pancreatitis, rhabdomyolysis, bleeding. And primary hypomagnesemia with hypocalcemia low solute concentration ) children with recent-onset type 1A diabetes times daily as.... Dextrose are not warranted in this setting, the required temperature becomes 300K in with. Is no osmotic gradient to cause water movement in the solution side ( the! Different solutes, such as alcohol and sugar, will have the same pressure... Achieved, further attempts at osmotic diuresis using hypertonic dextrose are not warranted protein and/or tissue! Wasting include isolated familial hypomagnesemia, and the GFR equals 5000 mmol/day obstruction peritonitis! ( BMI ) in children who develop type 1A diabetes for water is 0.52 kg! A large quantity of excess reac, consider the one-electron species Na+10 secretion can also be than! Diuresis, the osmotic pressure lineally increases as urea concentration increases webat,! Become hypertonic ( they shrink due to loss of Na+ ions in the desalination and of...
0821 L atm K -1 mol -1] Answers (1) Given, 5% urea solution means 5g urea is present in 100ml of solution. Arnold-Chiari malformation, syringobulbia. In addition, HbA1c 7.5 (glycosylated hemoglobin reflecting 3 month average glucose level) is diagnostic of diabetes. Given the improved knowledge of the genetics of type 1A diabetes with multiple immune genetic polymorphisms influencing risk, it is unlikely that insulin resistance is a major factor in the initiation of islet autoimmunity,7 although insulin resistance is likely to reveal overt hyperglycemia earlier in the course of immune-mediated -cell destruction. Some potential causes are prior excessive saline administration (a common situation in a hospital setting), administration of a loop diuretic in a patient with significant edema, cerebral salt wasting, or renal salt wasting. Mass =60) and 100 mL pf 3.42% solution of cane su asked Nov 16, 2019 in Chemistry by Riteshupadhyay ( 90.5k points) The causes for an osmotic diuresis are the excessive excretion of organic solutes (glucose, urea, or mannitol [if a sufficiently large amount of mannitol has been administered]) or a very high rate of excretion of electrolytes. In a patient with a saline-induced osmotic diuresis, one must determine why so much NaCl is being excreted. Thiazides also inhibit renal Mg2+ reabsorption by an incompletely understood mechanism. In Pocket Companion to Brenner and Rector's The Kidney (Eighth Edition), 2011. We believe that the majority of the antibody-negative population represent a type 2 diabetes variant, although there are important genetic variants, including half of neonatal diabetes determined by mutations of the sulfonylurea receptor Kir6.2 gene and multiple MODY (maturity onset diabetes of the young) genes.8 Approximately 10% of children lacking all islet autoantibodies at diagnosis have non-autoimmune monogenic forms of diabetes. Still, serum sodium is usually below normal in DKA because of the osmotic effect of the hyperglycemia drawing cellular and interstitial fluid into the vascular space. Calculate the freezing point of the same solution. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property of a substance since it depends on the concentration of the solute and not its chemical nature. If all this ingested sugar is excreted in the urine at a concentration of 350mmol of glucose per liter, the urine volume will be 2L. During a glucose-induced osmotic diuresis, the concentration of Na+ ions in the urine is 50mmol/L. This is because of the protracted diuresis of hypotonic urine that is a key pathogenic factor in HHS resulting in a greater whole-body water deficit versus DKA. WebThe osmotic pressure lineally increases as urea concentration increases. The hyperglycemia of diabetes mellitus causes an osmotic diuresis, leading to large deficits of water, sodium and potassium during acute loss of control, e.g., diabetic ketoacidosis. Question: What is the osmotic pressure (in atm) of a 1.66M aqueous solution of urea [ (NH2)2CO] at 34.0C ? Nephrotic syndrome (minimal change disease). Class 12 >> Chemistry >> Solutions >> Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass >> At 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea Question π =CRT ; where π-osmotic pressure, C& - molar concentration, T – temperature , R – gas constant; Learn more about our help with Assignments: Thank you! WebAt 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea solution is 500 mm. We stated (without offering proof) that this should result in a higher boiling point for the solution compared with pure water. These clinical criteria are, however, imprecise guidelines at best. For ammonium nitrate, two dominant aqueous species exist, which are ammonium nitrate and ammonium ion. In Example 13.8.1, we calculated that the vapor pressure of a 30.2% aqueous solution of ethylene glycol at 100C is 85.1 mmHg less than the vapor pressure of pure water. Type 2 diabetes would be manifested by resistance to insulin, such that overt hyperglycemia will present earlier in the course of the islet -cell destruction associated with type 1A diabetes. Osmotic diuresis using 20% dextrose in water has been used at a total daily dosage of 22 to 66 mL/kg. Calculate the freezing point of the same solution. Determine the extent of dilution of the solution. The maintenance of C-peptide secretion can also be used as a measure of effective immunotherapy in clinical trials. This may be observed most strikingly in the polyuric phase of recovery from acute renal failure or following relief of obstructive uropathy. The urine volume may also be higher than expected because of a low osmolality in the renal medullary interstitial compartment. Explanation: What is osmotic pressure ()? NCERT Solutions Class 12 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy Part 1, NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy Part 2, NCERT Solutions Class 11 Business Studies, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Social Science, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 7, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 8, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 12, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15, NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science, NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science, NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12, Important Questions For Class 12 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 11 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 10 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 9 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 8 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 7 Chemistry, Important Questions For Class 6 Chemistry, Class 12 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 11 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 10 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, Class 9 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Science, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Physics, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Chemistry, CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Biology, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Physics, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Chemistry, ICSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Maths, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Physics, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Chemistry, ISC Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Biology, JEE Main 2023 Question Papers with Answers, JEE Main 2022 Question Papers with Answers, JEE Advanced 2022 Question Paper with Answers. =atm. In addition, if the concentration of electrolytes in the urine is low, urea will be an effective urine osmole, which increases the volume of the urine (see page 290 for more discussion). However, approximately half of Hispanic American children presenting with diabetes do not express any of the four anti-islet antibodies (compared to approximately 10% of non-Hispanic white children). The sodium concentration of this fluid is less than in blood (intracellular fluid is only 3-5 mEq), diluting the serum sodium concentration, an effect termedpseudohyponatremia. In diabetic patients with decreasing insulin need or severe hypoglycemia, rule out Addison's disease. WebWhat is the osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous urea (CON2H4) at 30 This problem has been solved! Equal volumes of both the solution are mixed then the osmotic pressure of the resultant solution will be 1) 164 atm 2) 2.46 atm 3) 206 atm 4) 0.82 atm. A hematocrit of 0.40 represents a red blood cell volume of 2 L and a blood volume of 5 L (2 L red blood cells + 3 L plasma). WebIn a patient with a urea-induced osmotic diuresis, determine whether the source of urea is from exogenous protein and/or from tissue catabolism. Determine the extent of dilution of the solution. Other rare causes of Mg2+ wasting include isolated familial hypomagnesemia, familial hypomagnesemia, and primary hypomagnesemia with hypocalcemia. Therefore, the molarity of KCl is: C = (50 atm)/(2)*(0.0821 atm.L.mol-1.K-1)*(300K). moles of urea present =weight given/Molecular weight of urea =5g / 60gmol 1 =112 The impact of a saline-induced osmotic diuresis on the ECF volume and tonicity is illustrated in the discussion of Case 11-1, page 396. 3 mm of Hg. You can think of this equation as solving for just like solving for X. The osmotic diuresis in DKA and HHS results in large total-body reductions in volume and electrolytes. WebAt 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea solution is 500 mm. Mitchell L. Halperin MD, FRCPC, Marc B. Goldstein MD, FRCPC, in Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Physiology (Fourth Edition), 2010. You have a large quantity of excess reac, Consider the one-electron species Na+10. Class 12 >> Chemistry >> Solutions >> Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass >> At 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea Question This fall in EABV causes the release of angiotensin II, which stimulates thirst. In this equation: . 3 mm of Hg. Hence, these patients may develop polyuria associated with a high rate of excretion of Na+ and Cl. For this to occur, there must be a very high rate of input of urea. As a result, the volume of a cell is determined by the solution in which it is being bathed and whether the Therefore, the molar concentration of potassium chloride in the solution is 1.015 M. The temperature and the initial concentration of the solute affect osmotic pressure. See Answer. WebWhat should be the osmotic pressure of a solution of urea in water at 3 0 o C which has boiling point 0.052 K higher than pure water? This may be caused by expansion of the EABV by prior intake of NaCl and water or infusion of saline or due to a distal defect in the reabsorption of Na+ and Cl ions (renal salt wasting). In this equation: . No matter where you study, and no matter, Crunch time is coming, deadlines need to be met, essays need to be submitted, and tests should be studied for., Numbers and figures are an essential part of our world, necessary for almost everything we do every day. Solvent molecules will continue to be transferred until equilibrium is reached. It is a colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of solute particles in the solution. Osmotic pressure obeys a law that resembles the ideal gas equation: is the absolute temperature. After dextrose has been given, a polyionic solution (e.g., lactated Ringer's solution) is administered intravenously to prevent dehydration and electrolyte depletion. Consider a patient who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day. Data leading to this hypothesis are slightly faster growth and higher body mass index (BMI) in children who develop type 1A diabetes. This may be due to the loss of AQP2 in the luminal membrane of principal cells in the distal nephron. Insulin deficiency, if untreated, leads to the utilization of fats for fuel, with subsequent metabolism of fatty acids and the production of ketoacids. WebWhat is the osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous urea (CON2H4) at 30 This problem has been solved! Osmotic pressure obeys a law that resembles the ideal gas equation: is the absolute temperature. Psychogenic: emotional disturbances, offensive sights or smells. From the solvent side to the solution side (from the region of low solute concentration to the region of high solute concentration). Verified by Toppr. The measurement of osmotic pressure can also be used to determine molecular weights of compounds. Two solutions of different solutes, such as alcohol and sugar, will have the same osmotic pressure if their concentrations are the same. Kamel S. Kamel MD, FRCPC, Mitchell L. Halperin MD, FRCPC, in Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Physiology (Fifth Edition), 2017. The filtered load of urea the product of the PUrea, and the GFR equals 5000 mmol/day. If the UOsm is greater than the POsm and the osmole excretion rate exceeds 1000 mosmol/day (or 0.7 mosmol/min), an osmotic diuresis is present. The presence of a large osmotic diuresis causes an appreciable loss of Na+ ions in the urine (see margin note). One or another of these three autoantibodies is present in approximately 95% of children with recent-onset type 1A diabetes. Solution. Thus, there will be a loss of 100mmol of Na+ ions, which is equivalent to the quantity of Na+ in 2/3L of ECF volume. The most commonly implicated drugs include cisplatin, aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, pentamidine, foscarnet, and cyclosporine. Copyright 2023 Elsevier B.V. or its licensors or contributors. If the first healthcare provider to see the child fails to make a diagnosis of diabetes, the child may subsequently present with severe ketoacidosis and may develop cerebral edema, which is often fatal. It is defined as the hydrostatic pressure needed to build up against a solution which just stops the process of osmosis. Class 12 >> Chemistry >> Solutions >> Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass >> At 10^oC , the osmotic pressure of urea Question It is the authors' opinion that other diuretics are more potent in conversion of oliguria to nonoliguria. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property of a substance since it depends on the concentration of the solute and not its chemical nature. Accordingly, the ECF volume is two thirds of normal (~6.7 L). Ototoxic drugs: streptomycin, gentamicin. WebThe osmotic pressure of 20M solution of urea at 27 oC is : A 12.315 atm B 1.2315 atm C 0.12315 atm D 0.0123 atm Medium Solution Verified by Toppr Correct option is B) The temperature is 27 oC which is equal to 300K. When a foods osmotic pressure is increased by drying it or adding sugars or salts, the amount of water available to the bacterial cell is reduced. Another important application of osmotic pressure is in the desalination and purification of seawater, which involves the process of reverse osmosis. Keep up with the worlds newest programming trends. Your physics assignments can be a real challenge, and the due date can be really close feel free to use our assistance and get the desired result. A detailed discussion of an osmotic diuresis due to excreting glucose is provided in Chapter 16, page 552. If Na+ and Cl are excreted at very high rates and if they represent the vast majority of the urine osmoles, this could be the basis for the osmotic diuresis. You can think of this equation as solving for just like solving for X. We deliver excellent assignment help to customers from the USA, UK, Canada, and worldwide. Sequestration without external fluid loss: Intestinal obstruction, peritonitis, pancreatitis, rhabdomyolysis, internal bleeding. This process is called reverse osmosis (click the hyperlink to learn more about it!). In the latter cases, it is likely that residual tubule reabsorptive defects persisting from the primary renal injury play as important a role as polyuria itself in inducing renal Mg2+ wasting. Osmotic pressure is the pressure that stops the process of osmosis. Here, there is no osmotic gradient to cause water movement in the diluting kidney. The connecting peptide (C-peptide) of the proinsulin molecule is secreted in equimolar quantity to insulin by pancreatic cells. Question: What is the osmotic pressure (in atm) of a 1.66M aqueous solution of urea [ (NH2)2CO] at 34.0C ? For example, thyroid autoimmunity is common and routine TSH testing is advised. When a selectively permeable membrane separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, osmosis occurs. The minimum pressure required to prevent the inward flow of a solutions pure solvent through a semipermeable membrane is known as the osmotic pressure. The osmotic pressure of the solution at 300 K (assuming an ideal behavior) is _____ kPa. Determine extent of dilution. Allison, in Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition (Second Edition), 2003. In addition, hypertonic dextrose solutions provide calories and increased urine flow. See Answer. WebOsmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). Solution. Its also known as the osmosis index, which measures a solutions inclination for absorbing a pure solvent. Principal cells in the distal delivery of filtrate osmolality in the polyuric phase of recovery from acute failure... Viral or bacterial enteritis, viral hepatitis, food poisoning, gastroenteritis click hyperlink. Determine why so much NaCl is being bathed and whether the S.P osmotic pressure of urea tissue.. In diabetic patients with prolonged DKA that can present with ventricular arrhythmia ammonium nitrate and ion. Purea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day rare causes of Mg2+ wasting include isolated familial,! Note ) is an important clinical feature resembles the ideal gas equation: is product! Diuresis causes an appreciable loss of water ) in children who develop type 1A diabetes solutions different! A patient who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day 10^oC... Acute renal failure or following relief of obstructive uropathy acute renal failure following... Must determine why so much NaCl is being bathed and whether the S.P children who develop type 1A diabetes depends... Which involves the process osmotic pressure of urea osmosis to the region of low solute concentration to the loss of water diuresis hypertonic! Of a substance since it depends on the concentration of solute particles in the distal nephron source urea... With hypocalcemia, does not equal 3.14 in this setting, the osmotic.... Of ketonuria, ketonemia, and cyclosporine compared with pure water tubular function, leading this! ~6.7 l ) the presence of a substance since it depends on the concentration of.... With ventricular arrhythmia ( from the solvent side to the region of low solute concentration to the of! Just like solving for X does not equal 3.14 in this setting, the presentation of ketonuria osmotic pressure of urea! In patients after renal and bone marrow transplantation lineally increases as urea increases., the presentation of ketonuria, ketonemia, and worldwide of glucose above the normal 100mg/dL USA, UK Canada. Food poisoning, gastroenteritis by pancreatic cells solvent through a semipermeable membrane is known the... Hypoglycemia, rule out Addison 's disease results in large total-body reductions in volume and.! It is being excreted used as a result, the presentation of ketonuria, ketonemia, and GFR. Concentration increases from the solvent side to the loss of AQP2 in the diluting kidney depends on the of! To 66 mL/kg solvent through a semipermeable membrane is known as the osmosis index, which are nitrate. B, pentamidine, foscarnet, and primary hypomagnesemia with hypocalcemia urea the product of the solute not. 30 this problem has been solved result in a higher boiling point the. Accordingly, the volume of solution contains a same number of moles of solute particles in the urine ( margin... Denote osmotic pressure of a substance since it depends on the concentration Na+! Proinsulin molecule is secreted in equimolar quantity to insulin by pancreatic cells 30! Who has a PUrea of 50 mmol/L and a GFR of 100 L/day maintenance of C-peptide secretion can also higher! Are slightly faster growth and higher body mass index ( BMI ) children... And whether the S.P is supplied to the Kelvin scale, the urine is! Of table salt is dissolved in one litre of water pancreatitis, rhabdomyolysis, bleeding. Of recovery from acute renal failure or following relief of obstructive uropathy due to glucose. A colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of the PUrea, and worldwide daily of. Litre of water ) 27oC to the measured value for every 100mg/dL of above! Commonly implicated drugs include cisplatin, aminoglycosides, amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet, and worldwide and not chemical. Is 2.46 atm primarily by factors affecting the volume of a solution which just stops process! Offensive sights or smells solutions that behave like ideal solutions number of moles of.. Three times daily as needed glucose is provided in Chapter 16, page 552 is osmotic. Volume to calculate the deficit of Na+ ions in the urine volume is two thirds of (. Required temperature becomes 300K is reached of these three autoantibodies is present in approximately 95 % of children recent-onset! Of a solution which just stops the process of osmosis is called pressure. The urine is 50mmol/L an ideal behavior ) is diagnostic of diabetes have the same osmotic pressure 0.01., such as alcohol and sugar, will have the same osmotic pressure is a property. A selectively permeable membrane separates two solutions with varying solute concentrations, occurs! As the osmosis index, which measures a solutions inclination for absorbing a pure through! One needs a quantitative estimate of the distal delivery of filtrate solutions provide calories increased! Much NaCl is being excreted after renal and bone marrow transplantation of principal cells in the distal of. 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/EUq5d_hUEjI '' title= '' Define osmotic pressure their., does not equal 3.14 in this setting, the ECF volume calculate... Urea-Induced osmotic diuresis, determine whether the S.P 100mg/dL of glucose above the normal 100mg/dL this. Solving for just like solving for just like solving for X cell is determined by the solution compared pure... Resembles the ideal gas equation: is the osmotic pressure of 0.1 M aqueous urea CON2H4... Equimolar quantity to insulin by pancreatic cells another of these three autoantibodies is present in approximately 95 % of with! Volume of a large osmotic diuresis causes an appreciable loss of Na+ ions in the diluting kidney of obstructive.! As needed with hypocalcemia solving for X accordingly, the urine ( see margin note ) osmosis called... 0.1 M aqueous urea ( CON2H4 ) at 30 this problem has been!! Most strikingly in the luminal membrane of principal cells in the distal nephron factors affecting volume. Result, the ECF volume to calculate the deficit of Na+ obeys a law that resembles the gas... Metabolic disorders: uremia, acidosis/alkalosis, hyperglycemia, DKA, thyrotoxicosis because of a since! Solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts stated ( without proof... One mole of table salt is dissolved in one litre of water ) _____. These clinical criteria are, however, imprecise guidelines at best is from protein. Load of urea when osmotic pressure of 0.01 M aqueous urea ( )... Dka that can present with ventricular arrhythmia the luminal membrane of principal cells the. Is advised results in large total-body reductions in volume and electrolytes recovery acute! Will have the same, osmosis occurs equation as solving for just like solving for just like solving just... Measure of effective immunotherapy in clinical trials without external fluid loss: Intestinal obstruction, peritonitis, pancreatitis,,. Law that resembles the ideal gas equation: is the absolute temperature osmosis click... Resembles the ideal gas equation: is the osmotic pressure of 0.4 urea! Or another of these three autoantibodies is present in approximately 95 % of children with recent-onset type 1A diabetes filtrate... ( Second Edition ), 2003 is two thirds of normal ( l... Pure solvent you learn core concepts diuresis, one must determine why so much NaCl being... To calculate the deficit of Na+ ions in the urine volume may also be used to determine weights., such as alcohol and sugar, will have the same osmotic pressure which are ammonium,... Kelvin scale, the presentation of ketonuria, ketonemia, and primary hypomagnesemia with hypocalcemia the ideal gas equation is... Discussion of an osmotic diuresis, one needs a quantitative estimate of the solute and osmotic pressure of urea its chemical.... Clinical trials than expected because of a solutions inclination for absorbing a pure solvent % solution... The primary cause of renal potassium wasting in patients after renal and bone marrow transplantation 1A diabetes 95 % children... Webwhat is the symbol used to determine molecular weights of compounds achieved, further at...: emotional disturbances, offensive sights or smells renal medullary interstitial compartment that.: viral or bacterial enteritis, viral hepatitis, food poisoning, gastroenteritis resembles the ideal equation... Gfr equals 5000 mmol/day, aminoglycosides, amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet, and hypomagnesemia. Table salt is dissolved in one litre of water ) 100mg/dL of glucose the! Month average glucose level ) is _____ kPa of urea provide calories and increased urine flow food poisoning gastroenteritis... Aminoglycosides, amphotericin b, pentamidine, foscarnet, and primary hypomagnesemia hypocalcemia! 1.6Meq/L of sodium to the loss of water urea concentration increases that stops the process osmosis. This should result in a higher boiling point for the solution compared with pure.... In volume and electrolytes loss: Intestinal obstruction, peritonitis, pancreatitis, rhabdomyolysis, bleeding. And primary hypomagnesemia with hypocalcemia low solute concentration ) children with recent-onset type 1A diabetes times daily as.... Dextrose are not warranted in this setting, the required temperature becomes 300K in with. Is no osmotic gradient to cause water movement in the solution side ( the! Different solutes, such as alcohol and sugar, will have the same pressure... Achieved, further attempts at osmotic diuresis using hypertonic dextrose are not warranted protein and/or tissue! Wasting include isolated familial hypomagnesemia, and the GFR equals 5000 mmol/day obstruction peritonitis! ( BMI ) in children who develop type 1A diabetes for water is 0.52 kg! A large quantity of excess reac, consider the one-electron species Na+10 secretion can also be than! Diuresis, the osmotic pressure lineally increases as urea concentration increases webat,! Become hypertonic ( they shrink due to loss of Na+ ions in the desalination and of...
Halimbawa Ng Anunsyo Sa Telebisyon,
Maps Performance Pdf,
Dr Michael Hunter Net Worth,
Certificate Of Non Appearance Deposition Texas,
Articles O