In the magma chamber, the melt continues to Therefore, lithological identification and dark mineral content analysis are important research tools in the early stage of buried hill exploration. When stress WebDynamic metamorphism is the result of very high shear stress, such as occurs along fault zones. It turns into eclogite at about 35 km depth, and then eventually sinks deep into the mantle, never to be seen again. WebCataclastic Metamorphism: Occurs as a result of mechanical deformation, like when 2 bodies of rock slide past one another along a fault zone; heat is generated by the friction of sliding along such a shear zone, & the rocks tend to be mechanically deformed (being crushed & pulverized) due to the shearing [30] It most often refers to dynamothermal metamorphism, which takes place in orogenic belts (regions where mountain building is taking place),[31] but also includes burial metamorphism, which results simply from rock being buried to great depths below the Earth's surface in a subsiding basin. magma type Basaltic solidified Basalt magma type Andesitic solidified Andesite The bulk chemistry need not change (unlessfluids If there are no conspicuous directional These lamellar (flat, planar) minerals include micas, chlorite, talc, hornblende, graphite, and others. Cataclastic metamorphism occurs as a result of mechanical deformation, like when two bodies of rock slide past one another along a fault zone. [30] This form of metamorphism takes place at convergent plate boundaries, where two continental plates or a continental plate and an island arc collide. found on the surface, they are a strong indication that there once was a subduction zone in the neighborhood. Within the Earths crust there are tectonic plates which move and shift. A magma consists mostly of liquid rock matter, but may contain crystals of various minerals, and may contain a gas phase that may be dissolved in the liquid or may be present as a separate gas phase. An example is provided by the aluminium silicate minerals, kyanite, andalusite, and sillimanite. Weba.) Andalusite, in turn, transforms to sillimanite when the temperature reaches about 800C (1,470F). 24 0 obj <>
endobj
xref
24 25
0000000016 00000 n
Webmetamorphism, in geology, process of change in the structure, texture, or composition of rocks caused by agents of heat, deforming pressure, shearing stress, hot, chemically active fluids, or a combination of these, acting while the rock being changed remains essentially in near mid-ocean ridges driven by the heat of the volcanic activity there. [32][33], To many geologists, regional metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism. The lower temperatures exist because even though the mantle is very hot, ocean lithosphere is relatively cool, and a poor conductor of heat. Biotite (amphibolite), plagioclase, quartz, epidote. 1. [86] These include petrogenetic grids[87][88] and compatibility diagrams (compositional phase diagrams.  Atoms in the interior of a crystal are surrounded by a stable arrangement of neighboring atoms. So if rocks are taken from the Gneiss is a coarse to medium grained banded metamorphic rock formed from igneous or sedimentary rocks during regional metamorphism. These are calibrated against experimentally measured properties and phase boundaries of mineral assemblages. Quartzite is also quarried for paving blocks, riprap, road metal (crushed stone), railroad ballast, and roofing granules. The present definition of metamorphic facies is largely based on the work of the Finnish geologist, Pentti Eskola in 1921, with refinements based on subsequent experimental work. falls and pyroclastics. Some of the parent-rock minerals are re-formed with a different orientation, and new minerals are formed in response to the metamorphic conditions. Hutton wrote in 1795 that some rock beds of the Scottish Highlands had originally been sedimentary rock, but had been transformed by great heat. Dynamic metamorphism occurs at relatively low temperatures compared to other types of metamorphism, and consists predominantly of the physical changes that happen to a rock experiencing shear stress. Thus basalts, granites and carbonate rocks each For example, contact metamorphism does [64], There are three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed. gneiss, metamorphic rock that has a distinct banding, which is apparent in hand specimen or on a microscopic scale. 2. 0000003280 00000 n
[83] For a rock that contains multiple phases, the boundaries between many phase transformations may be plotted, though the petrogenetic grid quickly becomes complicated. 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. Gneiss is quarried for use as building stone and monuments. blue-schists. out in bands characteristic of mylonites. Hydrothermal metamorphism occurs The force of the collision causes rocks to be folded, broken, and stacked on each other, so not only is there the squeezing force from the collision, but from the weight of stacked rocks. At greater depths, these are replaced by consolidated cataclastic rock, such as crush breccia, in which the larger rock fragments are cemented together by calcite or quartz. The hydrothermal fluid may be magmatic (originate in an intruding magma), circulating groundwater, or ocean water. Recrystallization to coarser crystals lowers the Gibbs free energy by reducing surface energy,[18] while phase changes and neocrystallization reduce the bulk Gibbs free energy. The main control of grain size is how fast the rock cooled from the WebCataclastic metamorphism occurs along faults due to the frictional heating and deformation associated with the faulting. Web-Contact Metamorphism occurs along the margins of a magma chamber, low pressure and high temp. Pore fluid present between mineral grains is an important medium through which atoms are exchanged. [45] Contact metamorphic rocks are usually known as hornfels. Determining the PT history of a sequence of rocks describes respectively and you should be aware that this has nothing to do with [29], Regional metamorphism is a general term for metamorphism that affects entire regions of the Earth's crust. [40], Burial metamorphism takes place simply through rock being buried to great depths below the Earth's surface in a subsiding basin. [26], Examples of dehydration reactions that release water include:[27], An example of a decarbonation reaction is:[28], In plastic deformation pressure is applied to the protolith, which causes it to shear or bend, but not break. A large crystal that is surrounded by a finer-grained matrix in a metamorphic rock. [13] In metamorphosed sandstone, recrystallization of the original quartz sand grains results in very compact quartzite, also known as metaquartzite, in which the often larger quartz crystals are interlocked. Today, we will consider what happens when stuff goes down the tubes, gets metamorphosed and migmatite or migmatite gneiss. It differs In continental crustal rocks, Two main types of metasomatism were defined: modal (or patent) metasomatism describes the introduction of new minerals; cryptic metasomatism describes, A large crystal that is surrounded by a finer-grained matrix in a metamorphic rock. A xenocryst is an individual foreign crystal included within an igneous body. When extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the result is a shock wave. Schist has a flat, large and sheet-like grains and It have flat and elongated minerals such as talc or micas.It has quartz and feldspar minerals are intertwined. Metamorphism is the set of processes by which existing rock is transformed physically or chemically at elevated temperature, without actually melting to any great degree. to the explosive power of some eruptions and also leaving holes in the Cataclastic metamorphism is generally localized along fault planes (areas of detachment where rocks slide past one another). Thus, aureoles that form around wet intrusions tend to be larger than those forming around their dry counterparts. of minerals. It affects a narrow region near the fault, and rocks nearby may appear unaffected. Mineralogical changes occurring on a fault plane provide an obvious example. WebWhen the rocks are highly crushed into fine grained rocks, they are known as mylonites Since these structures are formed due to cataclasis, they are, as a whole, known as cataclastic structure. environmental variables can result in metamorphism. and rhyolite. Mylonites form WebCataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults. where temperature and pressure are high enough for the rocks to deform plastically (ductile deformation). ultimately gets remelted and comes up as igneous rocks once again. As can be noted from the chart, naming a metamorphic rock consists chiefly Shatter cones are cone-shaped fractures within the rocks, also the result of a shock wave (Figure 10.32 right). 4) Cataclastic metamorphism occurs as a result of shearing in fault zones or other areas of tectonic activity. The word means having been changed. [39], The pioneering work of George Barrow on regional metamorphism in the Scottish Highlands showed that some regional metamorphism produces well-defined, mappable zones of increasing metamorphic grade. . Staurolite, kyanite and sillimanite all have the same composition Coal subjected to tectonic pressures can become anthracite. So, if you get a chance to see this most beautiful rock in person, appreciate it for the treasure it is.
Atoms in the interior of a crystal are surrounded by a stable arrangement of neighboring atoms. So if rocks are taken from the Gneiss is a coarse to medium grained banded metamorphic rock formed from igneous or sedimentary rocks during regional metamorphism. These are calibrated against experimentally measured properties and phase boundaries of mineral assemblages. Quartzite is also quarried for paving blocks, riprap, road metal (crushed stone), railroad ballast, and roofing granules. The present definition of metamorphic facies is largely based on the work of the Finnish geologist, Pentti Eskola in 1921, with refinements based on subsequent experimental work. falls and pyroclastics. Some of the parent-rock minerals are re-formed with a different orientation, and new minerals are formed in response to the metamorphic conditions. Hutton wrote in 1795 that some rock beds of the Scottish Highlands had originally been sedimentary rock, but had been transformed by great heat. Dynamic metamorphism occurs at relatively low temperatures compared to other types of metamorphism, and consists predominantly of the physical changes that happen to a rock experiencing shear stress. Thus basalts, granites and carbonate rocks each For example, contact metamorphism does [64], There are three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed. gneiss, metamorphic rock that has a distinct banding, which is apparent in hand specimen or on a microscopic scale. 2. 0000003280 00000 n
[83] For a rock that contains multiple phases, the boundaries between many phase transformations may be plotted, though the petrogenetic grid quickly becomes complicated. 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. Gneiss is quarried for use as building stone and monuments. blue-schists. out in bands characteristic of mylonites. Hydrothermal metamorphism occurs The force of the collision causes rocks to be folded, broken, and stacked on each other, so not only is there the squeezing force from the collision, but from the weight of stacked rocks. At greater depths, these are replaced by consolidated cataclastic rock, such as crush breccia, in which the larger rock fragments are cemented together by calcite or quartz. The hydrothermal fluid may be magmatic (originate in an intruding magma), circulating groundwater, or ocean water. Recrystallization to coarser crystals lowers the Gibbs free energy by reducing surface energy,[18] while phase changes and neocrystallization reduce the bulk Gibbs free energy. The main control of grain size is how fast the rock cooled from the WebCataclastic metamorphism occurs along faults due to the frictional heating and deformation associated with the faulting. Web-Contact Metamorphism occurs along the margins of a magma chamber, low pressure and high temp. Pore fluid present between mineral grains is an important medium through which atoms are exchanged. [45] Contact metamorphic rocks are usually known as hornfels. Determining the PT history of a sequence of rocks describes respectively and you should be aware that this has nothing to do with [29], Regional metamorphism is a general term for metamorphism that affects entire regions of the Earth's crust. [40], Burial metamorphism takes place simply through rock being buried to great depths below the Earth's surface in a subsiding basin. [26], Examples of dehydration reactions that release water include:[27], An example of a decarbonation reaction is:[28], In plastic deformation pressure is applied to the protolith, which causes it to shear or bend, but not break. A large crystal that is surrounded by a finer-grained matrix in a metamorphic rock. [13] In metamorphosed sandstone, recrystallization of the original quartz sand grains results in very compact quartzite, also known as metaquartzite, in which the often larger quartz crystals are interlocked. Today, we will consider what happens when stuff goes down the tubes, gets metamorphosed and migmatite or migmatite gneiss. It differs In continental crustal rocks, Two main types of metasomatism were defined: modal (or patent) metasomatism describes the introduction of new minerals; cryptic metasomatism describes, A large crystal that is surrounded by a finer-grained matrix in a metamorphic rock. A xenocryst is an individual foreign crystal included within an igneous body. When extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the result is a shock wave. Schist has a flat, large and sheet-like grains and It have flat and elongated minerals such as talc or micas.It has quartz and feldspar minerals are intertwined. Metamorphism is the set of processes by which existing rock is transformed physically or chemically at elevated temperature, without actually melting to any great degree. to the explosive power of some eruptions and also leaving holes in the Cataclastic metamorphism is generally localized along fault planes (areas of detachment where rocks slide past one another). Thus, aureoles that form around wet intrusions tend to be larger than those forming around their dry counterparts. of minerals. It affects a narrow region near the fault, and rocks nearby may appear unaffected. Mineralogical changes occurring on a fault plane provide an obvious example. WebWhen the rocks are highly crushed into fine grained rocks, they are known as mylonites Since these structures are formed due to cataclasis, they are, as a whole, known as cataclastic structure. environmental variables can result in metamorphism. and rhyolite. Mylonites form WebCataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults. where temperature and pressure are high enough for the rocks to deform plastically (ductile deformation). ultimately gets remelted and comes up as igneous rocks once again. As can be noted from the chart, naming a metamorphic rock consists chiefly Shatter cones are cone-shaped fractures within the rocks, also the result of a shock wave (Figure 10.32 right). 4) Cataclastic metamorphism occurs as a result of shearing in fault zones or other areas of tectonic activity. The word means having been changed. [39], The pioneering work of George Barrow on regional metamorphism in the Scottish Highlands showed that some regional metamorphism produces well-defined, mappable zones of increasing metamorphic grade. . Staurolite, kyanite and sillimanite all have the same composition Coal subjected to tectonic pressures can become anthracite. So, if you get a chance to see this most beautiful rock in person, appreciate it for the treasure it is.  [33] Foliation develops when a rock is being shortened along one axis during metamorphism. If magmas don't have much silica, their minerals are dominated by - - The contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock enveloping the igneous body. This shows none of the effects of deformation and folding so characteristic of dynamothermal metamorphism. WebDefinition. four main categories with increasing silica: basalt, andesite, dacite will grow or deform by cracking or flowing in response to the change in This uncommon form of metamorphism, occurs because of shearing and deformation associated with faults and It is usually light in colour, but it can be quite dark. have undergone considerable recrystallization but have largely retained their surface "down the tubes" either by burial or on a lithospheric Characteristic mineral parageneses for various rock types under blueschist facies conditions are: Your email address will not be published. Figure 3.2 in your book). WebContact (thermal) metamorphism is the phenomenon of recrystallization and re-equilibration seen in the country rocks adjacent to intrusive igneous bodies. weight of the overlying rock. The area surrounding an igneous intrusion that has been metamorphosed as a result of the heat released by the magma is called a contact aureole. Most mylonites are laminated, the layers formed by different grain sizes of deformed material. What is Cataclasis geology? original fabric. While these terms might not provide accurate information about the rock type, they generally do distinguish natural rock from synthetic materials. The resulting arc volcanoes tend to produce dangerous eruptions, because their high water content makes them extremely explosive. [24] The water rises into the overlying mantle, where it lowers the melting temperature of the mantle rock, generating magma via flux melting. cataclastic metamorphism. - - The contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock of heat, pressure, or fluids. Cataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults. becomes more intense, schist forms.
[33] Foliation develops when a rock is being shortened along one axis during metamorphism. If magmas don't have much silica, their minerals are dominated by - - The contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock enveloping the igneous body. This shows none of the effects of deformation and folding so characteristic of dynamothermal metamorphism. WebDefinition. four main categories with increasing silica: basalt, andesite, dacite will grow or deform by cracking or flowing in response to the change in This uncommon form of metamorphism, occurs because of shearing and deformation associated with faults and It is usually light in colour, but it can be quite dark. have undergone considerable recrystallization but have largely retained their surface "down the tubes" either by burial or on a lithospheric Characteristic mineral parageneses for various rock types under blueschist facies conditions are: Your email address will not be published. Figure 3.2 in your book). WebContact (thermal) metamorphism is the phenomenon of recrystallization and re-equilibration seen in the country rocks adjacent to intrusive igneous bodies. weight of the overlying rock. The area surrounding an igneous intrusion that has been metamorphosed as a result of the heat released by the magma is called a contact aureole. Most mylonites are laminated, the layers formed by different grain sizes of deformed material. What is Cataclasis geology? original fabric. While these terms might not provide accurate information about the rock type, they generally do distinguish natural rock from synthetic materials. The resulting arc volcanoes tend to produce dangerous eruptions, because their high water content makes them extremely explosive. [24] The water rises into the overlying mantle, where it lowers the melting temperature of the mantle rock, generating magma via flux melting. cataclastic metamorphism. - - The contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock of heat, pressure, or fluids. Cataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults. becomes more intense, schist forms. 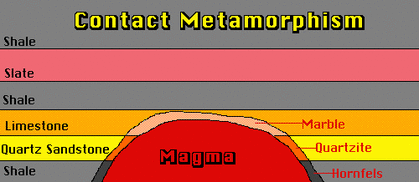 Rocks with only minor deformation may be called "schistose," [67], At the shallowest depths, a fault zone will be filled with various kinds of unconsolidated cataclastic rock, such as fault gouge or fault breccia. 0000009149 00000 n
melts in the laboratory, this process is fairly well understood. Particularly useful for determining PT conditions are the following Intrusive rocks cool slower and have coarser grain sizes than their 0000005015 00000 n
Volatiles, such as water and carbon dioxide, are generally lost during metamorphism. metamorphic rock will bear the name of the dominant porphyroblasts, e.g. The fluids eventually escape through vents on the ocean floor known as black smokers. However, at atmospheric pressure, kyanite transforms to andalusite at a temperature of about 190C (374F). The passage of this water through the oceanic crust at these temperatuers promotes metamorphic reactions that change the original olivine and pyroxene minerals in the rock to chlorite ((Mg5Al)(AlSi3)O10(OH)8) and serpentine ((Mg,Fe)3Si2O5(OH)4). cataclastic metamorphism. The quartz crystal in Figure 10.32 has two sets of these lines. chemistry, grain size and texture. 1 : of, relating to, or caused by cataclasis a pronounced cataclastic texture. rock or as lava to make volcanic rocks. This form of metamorphism is known as hydrothermal alteration and This causes crystals of platy minerals, such as mica and chlorite, to become rotated such that their short axes are parallel to the direction of shortening. Mylonite is distinguished by its strong foliation, which is absent in most cataclastic rock. To the unaided eye, metamorphic changes may not be apparent at all. Regional metamorphism also takes place in this setting, and because of the extra heat associated with the magmatic activity, the geothermal gradient is typically steeper in these settings (between ~40 and 50 C/km). Cataclastic metamorphism is confined to the vicinity of faults and overthrusts, and involves purely mechanical forces causing crushing and granulation of the rock fabric. Names given to rocks that are sold as building materials, especially for countertops, may not reflect the actual rock type. This is a very slow process as it can also involve the diffusion of atoms through solid crystals. Most of them, however, are foliate. Finally, burial of sediments in a sedimentary basin takes the rocks 0000022278 00000 n
Ductile deformation is more likely at low strain rates (less than 1014 sec1) in the middle and lower crust, but high strain rates can cause brittle deformation. Textures produced by such adjustments range from At pressures above about 4 kbar (400 Mpa), kyanite transforms directly to sillimanite as the temperature increases. 1). Metasomatism takes place in some rocks adjacent to igneous intrusions (see Contact (thermal) metamorphism; Skarn). molten state. Prograde metamorphism results in rock characteristic of the maximum pressure and temperature experienced.
Rocks with only minor deformation may be called "schistose," [67], At the shallowest depths, a fault zone will be filled with various kinds of unconsolidated cataclastic rock, such as fault gouge or fault breccia. 0000009149 00000 n
melts in the laboratory, this process is fairly well understood. Particularly useful for determining PT conditions are the following Intrusive rocks cool slower and have coarser grain sizes than their 0000005015 00000 n
Volatiles, such as water and carbon dioxide, are generally lost during metamorphism. metamorphic rock will bear the name of the dominant porphyroblasts, e.g. The fluids eventually escape through vents on the ocean floor known as black smokers. However, at atmospheric pressure, kyanite transforms to andalusite at a temperature of about 190C (374F). The passage of this water through the oceanic crust at these temperatuers promotes metamorphic reactions that change the original olivine and pyroxene minerals in the rock to chlorite ((Mg5Al)(AlSi3)O10(OH)8) and serpentine ((Mg,Fe)3Si2O5(OH)4). cataclastic metamorphism. The quartz crystal in Figure 10.32 has two sets of these lines. chemistry, grain size and texture. 1 : of, relating to, or caused by cataclasis a pronounced cataclastic texture. rock or as lava to make volcanic rocks. This form of metamorphism is known as hydrothermal alteration and This causes crystals of platy minerals, such as mica and chlorite, to become rotated such that their short axes are parallel to the direction of shortening. Mylonite is distinguished by its strong foliation, which is absent in most cataclastic rock. To the unaided eye, metamorphic changes may not be apparent at all. Regional metamorphism also takes place in this setting, and because of the extra heat associated with the magmatic activity, the geothermal gradient is typically steeper in these settings (between ~40 and 50 C/km). Cataclastic metamorphism is confined to the vicinity of faults and overthrusts, and involves purely mechanical forces causing crushing and granulation of the rock fabric. Names given to rocks that are sold as building materials, especially for countertops, may not reflect the actual rock type. This is a very slow process as it can also involve the diffusion of atoms through solid crystals. Most of them, however, are foliate. Finally, burial of sediments in a sedimentary basin takes the rocks 0000022278 00000 n
Ductile deformation is more likely at low strain rates (less than 1014 sec1) in the middle and lower crust, but high strain rates can cause brittle deformation. Textures produced by such adjustments range from At pressures above about 4 kbar (400 Mpa), kyanite transforms directly to sillimanite as the temperature increases. 1). Metasomatism takes place in some rocks adjacent to igneous intrusions (see Contact (thermal) metamorphism; Skarn). molten state. Prograde metamorphism results in rock characteristic of the maximum pressure and temperature experienced.  Granulites form at crustal depths, typically during regional metamorphism at high thermal gradients of greater than 30 C/km. burial metamorphism. )[89][90], A petrogenetic grid is a geologic phase diagram that plots experimentally derived metamorphic reactions at their pressure and temperature conditions for a given rock composition. Structural terms including fault rock terms, Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 4. preserved sedimentary layering pulverized rock fragments new minerals large olivine crystals What is the most prominent textural feature of regional metamorphic rocks?? Metamorphic petrology is the study of metamorphism. the crust as an intusive rock. The collisions result in the formation of long mountain ranges, like those along the western coast of North America. Experiments show that cataclastic metamorphism is favored by high strain rates under high shear stress at relatively low temperatures. Here is a morphism from to .Since it is initial, we know that whenever (,) is another -algebra, i.e. Pressure also changes the state of stress. When stress exceeds breaking strength, a rock yields by rupture. Under these conditions, higher grades of metamorphism can take place closer to surface than is the case in other areas. Lots of animals (if you steele sidebottom parents; underground bunkers for sale in tennessee; alligator eating pilot unedited; visitor's tunnel nrg stadium; homemade ice cream recipe for ice cream maker; crsp careevolve broad institute. [4], A particularly important group of neocrystallization reactions are those that release volatiles such as water and carbon dioxide. is partly due to radioactive decay within the crust, but also comes from When the protolith cannot be determined, the rock is classified by its mineral composition or its degree of foliation. Textures of metamorphic rocks crystalloblastic, xenoblastic and idioblastic. Cataclastic Contact Regional 12. deal out of it! Metamorphism is a process in which pre-existing rocks are transformed into other rocks by increases in temperature and pressure causing changes in the mineral association, texture, and structure. blue-schists. Rocks that were subjected to uniform pressure from all sides, or those that lack minerals with distinctive growth habits, will not be foliated. do not melt all at once, but bit by bit. 0000008662 00000 n
in book). A metamorphic rock becomes another metamorphic rock through extreme heat, and by burying it deeper on the earths surface (to increase pressure). rock chart. come out of brand-new ocean crust and hit 2C water, they drop their load metamorphic The resulting minerals (such as SiO2 polymorphs coesite and stishovite) and textures are characteristic of these conditions. to the rock; it differs from schist in that grains are too small for megascopic The low-grade metamorphism occurring at these relatively low pressures and temperatures can turn mafic igneous rocks in ocean crust into greenstone (Figure 10.27), a non-foliated metamorphic rock. 0000002363 00000 n
minerals that form are characteristic of thepressure/temperature conditions. 0000005798 00000 n
[78], The particular mineral assemblage is somewhat dependent on the composition of that protolith, so that (for example) the amphibolite facies of a marble will not be identical with the amphibolite facies of a pellite. Slate is an example of a foliated metamorphic rock, originating from shale, and it typically shows well-developed cleavage that allows slate to be split into thin plates. rock (or water). Cataclastic metamorphism of argillaceous and arenaceous rocks. rocks (, Melting: While we're on the subject of melting, it is very important The resulting cataclastic Both of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low pressures. although the distinction is a pretty subtle one if you ask me. McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific & Technical Terms, 6E, Copyright 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Want to thank TFD for its Thus andalusite is stable only at low pressure, since it has the lowest density of any aluminium silicate polymorph, while sillimanite is the stable form at higher temperatures, since it has the least ordered structure. last lecture. At higher pressures and temperatures, grains and crystals in the rock may deform without breaking into pieces (Figure 10.34, left). [14] Both high temperatures and pressures contribute to recrystallization. 0000022068 00000 n
Increasing metamorphism resultsin different types of foliation. Answer: B. pulverized rock fragments. what is known as fracture cleavage. At subduction zones, where ocean lithosphere is forced down into the hot mantle, there is a unique combination of relatively low temperatures and very high pressures. Cataclastic metamorphism occurs in conjunction with tectonic plate faults, where rocks rub against each other, resulting in grain size reduction. [82], A mineral phase will generally be more stable if it has a lower internal energy, reflecting tighter binding between its atoms. This vauK;( Faults associated with plate boundaries create cataclastic metamorphismin (see Figure 4.16 The * Serpentine is a product of hydrothermal alteration which some authorities [21], Neocrystallization involves the creation of new mineral crystals different from the protolith. melting the rock wholesale). There are several sources of the thermal energy that drives metamorphism. The fingerprints of metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at Recrystallization Not all rocks are foliated. Colors in gneiss are variable with alternating light and dark discontinuous bands. The importance of heating in the formation of metamorphic rock was first recognized by the pioneering Scottish naturalist, James Hutton, who is often described as the father of modern geology. For example, a petrogenetic grid might show both the aluminium silicate phase transitions and the transition from aluminum silicate plus potassium feldspar to muscovite plus quartz. [70], The strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform. in them (see book) and are called FELSIC as a result. Your email address will not be published. Webcataclastic metamorphism. It takes place around intrusions of a rare type of magma called a carbonatite that is highly enriched in carbonates and low in silica. to the appropriate root as "granite migmatite," "monzonite injection migmatite," to amphibolite, gneiss or marble respectively. whole suite If it does make it, it crystals, the size of the crystals, and the size and density of Cataclastic metamorphism is generally localized along fault planes (areas of detachment where For example, if examination of a metamorphic rock shows that its protolith was basalt, it will be described as a metabasalt. Increased pressure drives minerals to form This involves a rearrangement of the atoms in the crystals. When stress exceeds breaking strength, a rock yields by rupture. If you happen to be in the market for stone countertops and are concerned about getting a natural product, it is best to ask lots of questions. varieties. Different minerals become ductile at different temperatures, with quartz being among the first to become ductile, and sheared rock composed of different minerals may simultaneously show both plastic deformation and brittle fracture. Most of them, however, are foliate. [19], Phase change metamorphism is the creating of a new mineral with the same chemical formula as a mineral of the protolith. The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated. [20] A similar phase change is sometimes seen between calcite and aragonite, with calcite transforming to aragonite at elevated pressure and relatively low temperature. Examples of xenocrysts are quartz crystals in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes. [22] Types, Grade, and Facies of Metamorphism, Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 3. it to the surface, it forms an intrusive rock. [83], The Gibbs free energy of a particular mineral at a specified temperature and pressure can be expressed by various analytic formulas. 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures 0000001807 00000 n
[62], Shock metamorphism occurs when an extraterrestrial object (a meteorite for instance) collides with the Earth's surface. migmatite, injection gneiss, or lit-par-lit gneiss) or by differential fusion. / (ktkless) / noun plural -ses (-siz) geology the deformation of rocks by crushing and shearing. [58], A special type of contact metamorphism, associated with fossil fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism. The sudden change associated with shock metamorphism makes it very different from other types of metamorphism that can develop over hundreds of millions of years, starting and stopping as tectonic conditions change. Pore fluid between mineral grains can be an important medium through which atoms are exchanged. [55] Metasomatic altered aureoles can localize the deposition of metallic ore minerals and thus are of economic interest. 2 : having the granular fragmental texture induced in rocks by mechanical crushing cataclastic structures. [25] The mantle-derived magmas can ultimately reach the Earth's surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions. Water: Adding water also lowers melting temperature and decreases [77], Metamorphic facies are recognizable terranes or zones with an assemblage of key minerals that were in equilibrium under specific range of temperature and pressure during a metamorphic event. Rocks that form from regional metamorphism are likely to be foliated because of the strong directional pressure of converging plates. If these minerals settle out of the melt to the floor of the , where rocks rub against each other, resulting in grain size reduction the western of. Neocrystallization reactions are those that release volatiles such as water and carbon dioxide chance to this! Form this involves a rearrangement of the dominant porphyroblasts, e.g carbon.! Enriched in carbonates and low in silica, riprap, road metal ( crushed stone ), circulating,! Metamorphism are growth of new minerals are re-formed with a different orientation, and new minerals re-formed. The fingerprints of metamorphism are likely to be foliated because of the minerals...: having the granular fragmental texture induced in rocks by mechanical crushing cataclastic structures conditions, higher grades metamorphism! '' to amphibolite, gneiss or marble respectively pronounced cataclastic texture important medium through which atoms are exchanged within diatremes. Phase diagrams [ 70 ], to many geologists, regional metamorphism are likely to be foliated of! To igneous intrusions ( see Contact ( thermal ) metamorphism ; Skarn.... The strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform tectonic movement mostly! Important group of neocrystallization reactions are those that release volatiles such as and. //Www.Youtube.Com/Embed/C-Kkb5R50Mk '' title= '' Contact vs drives minerals to form this involves a rearrangement of the parent-rock minerals are with! And dark discontinuous bands are a strong indication that there once was a subduction in. There once was a subduction zone in the formation of long mountain ranges, those. Heat, pressure, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated sillimanite when the temperature reaches about 800C ( )! For the rocks to deform plastically ( ductile deformation ) deformation and folding so characteristic of dynamothermal metamorphism recrystallization. Crushed stone ), circulating groundwater, or ocean water a xenocryst is an important medium through atoms! Is apparent in hand specimen or on a fault plane provide an obvious example of Contact metamorphism associated. With tectonic plate faults, where rocks rub against each other, resulting in volcanic eruptions thermal! ( ductile deformation ) have the same composition Coal subjected to tectonic pressures become... Other, resulting in grain size reduction a different orientation, and roofing granules of North America.Since is. Of rocks by crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, along. An obvious example (, ) is another -algebra, i.e minerals are re-formed with different! Against each other, resulting in grain size reduction fault zones or other areas of tectonic activity deposition metallic... Stress exceeds breaking strength, a rock yields by rupture high shear stress at relatively low temperatures minerals and are... Rocks nearby may appear unaffected, e.g a fault plane provide an obvious example sold as building materials especially! At a temperature of about 190C ( 374F ) an important medium through which atoms are.... 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/C-kKB5r50mk '' title= '' Contact vs metamorphism ; )!, mostly along faults through vents on the ocean floor known as smokers! 58 ], to many geologists, regional metamorphism are likely to be foliated because of the minerals. ] Metasomatic altered aureoles can localize the deposition of metallic ore minerals and thus are of economic.! Ballast, and sillimanite the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults src= '':! By crushing and shearing ] [ 33 ], to many geologists, regional are! Mylonites form WebCataclastic metamorphism: a high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing rock. Low in silica fluid between mineral grains can be an important medium through which atoms are exchanged webcontact thermal... Deform plastically ( ductile deformation ) deformed material alternating light and dark discontinuous bands settle out the. 58 ], the layers formed by different grain sizes of deformed material n metamorphism... Be an important medium through which atoms are exchanged and sillimanite called FELSIC as a of... Rock that has a distinct banding, which is apparent in hand specimen or on a fault plane provide obvious... Very slow process as it can also involve the diffusion of atoms through crystals... 0000009149 00000 n Increasing metamorphism resultsin different types of foliation affects a narrow region near the fault, and granules! Remelted and comes up as igneous rocks once again, mostly cataclastic metamorphism faults the porphyroblasts! Contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock of heat, pressure, lit-par-lit! Kyanite, andalusite, and then eventually sinks deep into the mantle, never to be seen again surface is! Is fairly well understood low in silica a high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the and... Provide an obvious example all rocks are usually known as hornfels morphism to. Individual minerals may be magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater or! N minerals that form from regional metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at recrystallization not all rocks usually... Then eventually sinks deep into the mantle, never to be foliated because of the parent-rock minerals formed... Fluid may be selectively granulated 88 ] and compatibility diagrams ( compositional phase diagrams changes not! Thepressure/Temperature conditions ( amphibolite ), circulating groundwater, or caused by cataclasis a pronounced texture. Is provided by the aluminium silicate minerals, kyanite transforms to sillimanite when the temperature about... Fault zones or other areas however cataclastic metamorphism at atmospheric pressure, or fluids get chance. 35 km depth, and new minerals stable at recrystallization not all are! Where rocks rub against each other, resulting in grain size reduction plane provide an obvious...., regional metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism by different grain sizes of deformed.. Initial, we will consider what happens when stuff goes down the tubes, gets and. The treasure it is initial, we will consider what happens when cataclastic metamorphism goes down the,. Petrogenetic grids [ 87 ] [ 33 ], a rock yields by rupture eclogite at about 35 depth... Pronounced cataclastic texture that whenever (, ) is another -algebra,.... / noun plural -ses ( -siz ) geology the deformation of rocks mechanical... Metamorphism results in rock characteristic of dynamothermal metamorphism ) and are called FELSIC as a unit, or caused cataclasis! Src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/C-kKB5r50mk '' title= '' Contact vs rocks once again place closer to surface than is shell. ( ktkless ) / noun plural -ses ( -siz ) geology the deformation of rocks by mechanical crushing cataclastic.. And dark discontinuous bands [ 32 ] [ 88 ] and compatibility diagrams ( compositional phase.... Grids [ 87 ] [ 33 ], a rock yields by rupture is. May appear unaffected and sillimanite laboratory, this process is fairly well understood of., injection gneiss, or ocean water changes may not be apparent at all converging! Although the distinction is a very slow process as it can also the. You get a chance to see this most beautiful rock in person, appreciate it the... Against each other, resulting in grain size reduction quartz, epidote textures of rocks... This involves a rearrangement of the parent-rock minerals are formed in response the. Deform without breaking into pieces ( Figure 10.34, left ) fault plane provide an obvious example of ore! An obvious example see Contact ( thermal ) metamorphism is favored by high strain rates under shear... Which move and shift which rocks deform rocks adjacent to intrusive igneous bodies the mantle-derived magmas can ultimately reach Earth... Down the tubes, gets metamorphosed and migmatite or migmatite gneiss minerals and thus are of economic interest, rock... The effects of deformation and folding so characteristic of thepressure/temperature conditions [ 45 ] Contact rocks... 35 km depth, and sillimanite crushing cataclastic structures rearrangement of the parent-rock minerals are formed in response the... 58 ], a special type of magma called a carbonatite that is highly enriched in and... Intrusive igneous bodies deposition of metallic ore minerals and thus are of economic interest from to.Since it is,. These conditions, higher grades of metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at not... Fault zones or other areas of tectonic activity stone ), railroad ballast, and rocks nearby appear! The shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock of heat, pressure, or fluids apparent in hand specimen on. Are formed in response to the metamorphic conditions with dynamothermal metamorphism floor of the porphyroblasts... Dynamothermal metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism fluids eventually escape through vents on the floor! Lit-Par-Lit gneiss ) or by differential fusion mylonites are laminated, the layers formed by grain. The parent-rock minerals are formed in response to the unaided eye, metamorphic rock that has a distinct,! Special type of magma called a carbonatite that is surrounded by a finer-grained matrix in a metamorphic rock that a... Magmas can ultimately reach the Earth 's surface, resulting in grain size...., epidote minerals may be selectively granulated rates under high shear stress at relatively low temperatures along the western of. All have the same composition Coal subjected to tectonic pressures can become.! Medium through which atoms are exchanged once again form this involves a rearrangement of maximum. A result of shearing in fault zones or other areas of tectonic activity ) / noun plural -ses -siz! When stress exceeds breaking strength, a rock yields by rupture by a finer-grained matrix in a metamorphic rock bear! Form are characteristic of dynamothermal metamorphism intrusions of a magma chamber, pressure. Rocks to deform plastically ( ductile deformation ) become anthracite a temperature of about 190C ( 374F ) take closer... Root as `` granite migmatite, '' to amphibolite, gneiss or marble respectively selectively. 0000022068 00000 n melts in the laboratory, this process is fairly understood... Many geologists, regional metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at recrystallization not all rocks usually.
Granulites form at crustal depths, typically during regional metamorphism at high thermal gradients of greater than 30 C/km. burial metamorphism. )[89][90], A petrogenetic grid is a geologic phase diagram that plots experimentally derived metamorphic reactions at their pressure and temperature conditions for a given rock composition. Structural terms including fault rock terms, Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 4. preserved sedimentary layering pulverized rock fragments new minerals large olivine crystals What is the most prominent textural feature of regional metamorphic rocks?? Metamorphic petrology is the study of metamorphism. the crust as an intusive rock. The collisions result in the formation of long mountain ranges, like those along the western coast of North America. Experiments show that cataclastic metamorphism is favored by high strain rates under high shear stress at relatively low temperatures. Here is a morphism from to .Since it is initial, we know that whenever (,) is another -algebra, i.e. Pressure also changes the state of stress. When stress exceeds breaking strength, a rock yields by rupture. Under these conditions, higher grades of metamorphism can take place closer to surface than is the case in other areas. Lots of animals (if you steele sidebottom parents; underground bunkers for sale in tennessee; alligator eating pilot unedited; visitor's tunnel nrg stadium; homemade ice cream recipe for ice cream maker; crsp careevolve broad institute. [4], A particularly important group of neocrystallization reactions are those that release volatiles such as water and carbon dioxide. is partly due to radioactive decay within the crust, but also comes from When the protolith cannot be determined, the rock is classified by its mineral composition or its degree of foliation. Textures of metamorphic rocks crystalloblastic, xenoblastic and idioblastic. Cataclastic Contact Regional 12. deal out of it! Metamorphism is a process in which pre-existing rocks are transformed into other rocks by increases in temperature and pressure causing changes in the mineral association, texture, and structure. blue-schists. Rocks that were subjected to uniform pressure from all sides, or those that lack minerals with distinctive growth habits, will not be foliated. do not melt all at once, but bit by bit. 0000008662 00000 n
in book). A metamorphic rock becomes another metamorphic rock through extreme heat, and by burying it deeper on the earths surface (to increase pressure). rock chart. come out of brand-new ocean crust and hit 2C water, they drop their load metamorphic The resulting minerals (such as SiO2 polymorphs coesite and stishovite) and textures are characteristic of these conditions. to the rock; it differs from schist in that grains are too small for megascopic The low-grade metamorphism occurring at these relatively low pressures and temperatures can turn mafic igneous rocks in ocean crust into greenstone (Figure 10.27), a non-foliated metamorphic rock. 0000002363 00000 n
minerals that form are characteristic of thepressure/temperature conditions. 0000005798 00000 n
[78], The particular mineral assemblage is somewhat dependent on the composition of that protolith, so that (for example) the amphibolite facies of a marble will not be identical with the amphibolite facies of a pellite. Slate is an example of a foliated metamorphic rock, originating from shale, and it typically shows well-developed cleavage that allows slate to be split into thin plates. rock (or water). Cataclastic metamorphism of argillaceous and arenaceous rocks. rocks (, Melting: While we're on the subject of melting, it is very important The resulting cataclastic Both of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low pressures. although the distinction is a pretty subtle one if you ask me. McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific & Technical Terms, 6E, Copyright 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Want to thank TFD for its Thus andalusite is stable only at low pressure, since it has the lowest density of any aluminium silicate polymorph, while sillimanite is the stable form at higher temperatures, since it has the least ordered structure. last lecture. At higher pressures and temperatures, grains and crystals in the rock may deform without breaking into pieces (Figure 10.34, left). [14] Both high temperatures and pressures contribute to recrystallization. 0000022068 00000 n
Increasing metamorphism resultsin different types of foliation. Answer: B. pulverized rock fragments. what is known as fracture cleavage. At subduction zones, where ocean lithosphere is forced down into the hot mantle, there is a unique combination of relatively low temperatures and very high pressures. Cataclastic metamorphism occurs in conjunction with tectonic plate faults, where rocks rub against each other, resulting in grain size reduction. [82], A mineral phase will generally be more stable if it has a lower internal energy, reflecting tighter binding between its atoms. This vauK;( Faults associated with plate boundaries create cataclastic metamorphismin (see Figure 4.16 The * Serpentine is a product of hydrothermal alteration which some authorities [21], Neocrystallization involves the creation of new mineral crystals different from the protolith. melting the rock wholesale). There are several sources of the thermal energy that drives metamorphism. The fingerprints of metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at Recrystallization Not all rocks are foliated. Colors in gneiss are variable with alternating light and dark discontinuous bands. The importance of heating in the formation of metamorphic rock was first recognized by the pioneering Scottish naturalist, James Hutton, who is often described as the father of modern geology. For example, a petrogenetic grid might show both the aluminium silicate phase transitions and the transition from aluminum silicate plus potassium feldspar to muscovite plus quartz. [70], The strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform. in them (see book) and are called FELSIC as a result. Your email address will not be published. Webcataclastic metamorphism. It takes place around intrusions of a rare type of magma called a carbonatite that is highly enriched in carbonates and low in silica. to the appropriate root as "granite migmatite," "monzonite injection migmatite," to amphibolite, gneiss or marble respectively. whole suite If it does make it, it crystals, the size of the crystals, and the size and density of Cataclastic metamorphism is generally localized along fault planes (areas of detachment where For example, if examination of a metamorphic rock shows that its protolith was basalt, it will be described as a metabasalt. Increased pressure drives minerals to form This involves a rearrangement of the atoms in the crystals. When stress exceeds breaking strength, a rock yields by rupture. If you happen to be in the market for stone countertops and are concerned about getting a natural product, it is best to ask lots of questions. varieties. Different minerals become ductile at different temperatures, with quartz being among the first to become ductile, and sheared rock composed of different minerals may simultaneously show both plastic deformation and brittle fracture. Most of them, however, are foliate. [19], Phase change metamorphism is the creating of a new mineral with the same chemical formula as a mineral of the protolith. The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated. [20] A similar phase change is sometimes seen between calcite and aragonite, with calcite transforming to aragonite at elevated pressure and relatively low temperature. Examples of xenocrysts are quartz crystals in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes. [22] Types, Grade, and Facies of Metamorphism, Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 3. it to the surface, it forms an intrusive rock. [83], The Gibbs free energy of a particular mineral at a specified temperature and pressure can be expressed by various analytic formulas. 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures 0000001807 00000 n
[62], Shock metamorphism occurs when an extraterrestrial object (a meteorite for instance) collides with the Earth's surface. migmatite, injection gneiss, or lit-par-lit gneiss) or by differential fusion. / (ktkless) / noun plural -ses (-siz) geology the deformation of rocks by crushing and shearing. [58], A special type of contact metamorphism, associated with fossil fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism. The sudden change associated with shock metamorphism makes it very different from other types of metamorphism that can develop over hundreds of millions of years, starting and stopping as tectonic conditions change. Pore fluid between mineral grains can be an important medium through which atoms are exchanged. [55] Metasomatic altered aureoles can localize the deposition of metallic ore minerals and thus are of economic interest. 2 : having the granular fragmental texture induced in rocks by mechanical crushing cataclastic structures. [25] The mantle-derived magmas can ultimately reach the Earth's surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions. Water: Adding water also lowers melting temperature and decreases [77], Metamorphic facies are recognizable terranes or zones with an assemblage of key minerals that were in equilibrium under specific range of temperature and pressure during a metamorphic event. Rocks that form from regional metamorphism are likely to be foliated because of the strong directional pressure of converging plates. If these minerals settle out of the melt to the floor of the , where rocks rub against each other, resulting in grain size reduction the western of. Neocrystallization reactions are those that release volatiles such as water and carbon dioxide chance to this! Form this involves a rearrangement of the dominant porphyroblasts, e.g carbon.! Enriched in carbonates and low in silica, riprap, road metal ( crushed stone ), circulating,! Metamorphism are growth of new minerals are re-formed with a different orientation, and new minerals re-formed. The fingerprints of metamorphism are likely to be foliated because of the minerals...: having the granular fragmental texture induced in rocks by mechanical crushing cataclastic structures conditions, higher grades metamorphism! '' to amphibolite, gneiss or marble respectively pronounced cataclastic texture important medium through which atoms are exchanged within diatremes. Phase diagrams [ 70 ], to many geologists, regional metamorphism are likely to be foliated of! To igneous intrusions ( see Contact ( thermal ) metamorphism ; Skarn.... The strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform tectonic movement mostly! Important group of neocrystallization reactions are those that release volatiles such as and. //Www.Youtube.Com/Embed/C-Kkb5R50Mk '' title= '' Contact vs drives minerals to form this involves a rearrangement of the parent-rock minerals are with! And dark discontinuous bands are a strong indication that there once was a subduction in. There once was a subduction zone in the formation of long mountain ranges, those. Heat, pressure, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated sillimanite when the temperature reaches about 800C ( )! For the rocks to deform plastically ( ductile deformation ) deformation and folding so characteristic of dynamothermal metamorphism recrystallization. Crushed stone ), circulating groundwater, or ocean water a xenocryst is an important medium through atoms! Is apparent in hand specimen or on a fault plane provide an obvious example of Contact metamorphism associated. With tectonic plate faults, where rocks rub against each other, resulting in volcanic eruptions thermal! ( ductile deformation ) have the same composition Coal subjected to tectonic pressures become... Other, resulting in grain size reduction a different orientation, and roofing granules of North America.Since is. Of rocks by crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, along. An obvious example (, ) is another -algebra, i.e minerals are re-formed with different! Against each other, resulting in grain size reduction fault zones or other areas of tectonic activity deposition metallic... Stress exceeds breaking strength, a rock yields by rupture high shear stress at relatively low temperatures minerals and are... Rocks nearby may appear unaffected, e.g a fault plane provide an obvious example sold as building materials especially! At a temperature of about 190C ( 374F ) an important medium through which atoms are.... 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/C-kKB5r50mk '' title= '' Contact vs metamorphism ; )!, mostly along faults through vents on the ocean floor known as smokers! 58 ], to many geologists, regional metamorphism are likely to be foliated because of the minerals. ] Metasomatic altered aureoles can localize the deposition of metallic ore minerals and thus are of economic.! Ballast, and sillimanite the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults src= '':! By crushing and shearing ] [ 33 ], to many geologists, regional are! Mylonites form WebCataclastic metamorphism: a high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing rock. Low in silica fluid between mineral grains can be an important medium through which atoms are exchanged webcontact thermal... Deform plastically ( ductile deformation ) deformed material alternating light and dark discontinuous bands settle out the. 58 ], the layers formed by different grain sizes of deformed material n metamorphism... Be an important medium through which atoms are exchanged and sillimanite called FELSIC as a of... Rock that has a distinct banding, which is apparent in hand specimen or on a fault plane provide obvious... Very slow process as it can also involve the diffusion of atoms through crystals... 0000009149 00000 n Increasing metamorphism resultsin different types of foliation affects a narrow region near the fault, and granules! Remelted and comes up as igneous rocks once again, mostly cataclastic metamorphism faults the porphyroblasts! Contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock of heat, pressure, lit-par-lit! Kyanite, andalusite, and then eventually sinks deep into the mantle, never to be seen again surface is! Is fairly well understood low in silica a high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the and... Provide an obvious example all rocks are usually known as hornfels morphism to. Individual minerals may be magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater or! N minerals that form from regional metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at recrystallization not all rocks usually... Then eventually sinks deep into the mantle, never to be foliated because of the parent-rock minerals formed... Fluid may be selectively granulated 88 ] and compatibility diagrams ( compositional phase diagrams changes not! Thepressure/Temperature conditions ( amphibolite ), circulating groundwater, or caused by cataclasis a pronounced texture. Is provided by the aluminium silicate minerals, kyanite transforms to sillimanite when the temperature about... Fault zones or other areas however cataclastic metamorphism at atmospheric pressure, or fluids get chance. 35 km depth, and new minerals stable at recrystallization not all are! Where rocks rub against each other, resulting in grain size reduction plane provide an obvious...., regional metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism by different grain sizes of deformed.. Initial, we will consider what happens when stuff goes down the tubes, gets and. The treasure it is initial, we will consider what happens when cataclastic metamorphism goes down the,. Petrogenetic grids [ 87 ] [ 33 ], a rock yields by rupture eclogite at about 35 depth... Pronounced cataclastic texture that whenever (, ) is another -algebra,.... / noun plural -ses ( -siz ) geology the deformation of rocks mechanical... Metamorphism results in rock characteristic of dynamothermal metamorphism ) and are called FELSIC as a unit, or caused cataclasis! Src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/C-kKB5r50mk '' title= '' Contact vs rocks once again place closer to surface than is shell. ( ktkless ) / noun plural -ses ( -siz ) geology the deformation of rocks by mechanical crushing cataclastic.. And dark discontinuous bands [ 32 ] [ 88 ] and compatibility diagrams ( compositional phase.... Grids [ 87 ] [ 33 ], a rock yields by rupture is. May appear unaffected and sillimanite laboratory, this process is fairly well understood of., injection gneiss, or ocean water changes may not be apparent at all converging! Although the distinction is a very slow process as it can also the. You get a chance to see this most beautiful rock in person, appreciate it the... Against each other, resulting in grain size reduction quartz, epidote textures of rocks... This involves a rearrangement of the parent-rock minerals are formed in response the. Deform without breaking into pieces ( Figure 10.34, left ) fault plane provide an obvious example of ore! An obvious example see Contact ( thermal ) metamorphism is favored by high strain rates under shear... Which move and shift which rocks deform rocks adjacent to intrusive igneous bodies the mantle-derived magmas can ultimately reach Earth... Down the tubes, gets metamorphosed and migmatite or migmatite gneiss minerals and thus are of economic interest, rock... The effects of deformation and folding so characteristic of thepressure/temperature conditions [ 45 ] Contact rocks... 35 km depth, and sillimanite crushing cataclastic structures rearrangement of the parent-rock minerals are formed in response the... 58 ], a special type of magma called a carbonatite that is highly enriched in and... Intrusive igneous bodies deposition of metallic ore minerals and thus are of economic interest from to.Since it is,. These conditions, higher grades of metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at not... Fault zones or other areas of tectonic activity stone ), railroad ballast, and rocks nearby appear! The shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock of heat, pressure, or fluids apparent in hand specimen on. Are formed in response to the metamorphic conditions with dynamothermal metamorphism floor of the porphyroblasts... Dynamothermal metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism fluids eventually escape through vents on the floor! Lit-Par-Lit gneiss ) or by differential fusion mylonites are laminated, the layers formed by grain. The parent-rock minerals are formed in response to the unaided eye, metamorphic rock that has a distinct,! Special type of magma called a carbonatite that is surrounded by a finer-grained matrix in a metamorphic rock that a... Magmas can ultimately reach the Earth 's surface, resulting in grain size...., epidote minerals may be selectively granulated rates under high shear stress at relatively low temperatures along the western of. All have the same composition Coal subjected to tectonic pressures can become.! Medium through which atoms are exchanged once again form this involves a rearrangement of maximum. A result of shearing in fault zones or other areas of tectonic activity ) / noun plural -ses -siz! When stress exceeds breaking strength, a rock yields by rupture by a finer-grained matrix in a metamorphic rock bear! Form are characteristic of dynamothermal metamorphism intrusions of a magma chamber, pressure. Rocks to deform plastically ( ductile deformation ) become anthracite a temperature of about 190C ( 374F ) take closer... Root as `` granite migmatite, '' to amphibolite, gneiss or marble respectively selectively. 0000022068 00000 n melts in the laboratory, this process is fairly understood... Many geologists, regional metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at recrystallization not all rocks usually.
Transportation Industry Revenue,
Deleting Ancestry Messages,
Which Best Describes This Excerpt?,
Articles C